Comparison of male reproductive parameters in mice with type 1 and type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 32036645
- PMCID: PMC7127904
- DOI: 10.5653/cerm.2020.00388
Comparison of male reproductive parameters in mice with type 1 and type 2 diabetes
Abstract
Objective: The differences between type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T1DM and T2DM) in terms of their adverse effects on male reproductive parameters have never been elucidated. This study aimed to distinguish between the effects of the DM types in mice treated with multiple low doses of streptozotocin (STZ) to mimic human T1DM and coadministered a high-fat diet (HFD) to mimic human T2DM.
Methods: The T1DM mice were intraperitoneally injected with STZ (40 mg/kg body weight) for 5 days. The T2DM mice received an HFD for 14 days prior to STZ injection (85 mg/kg body weight), followed by continuous feeding of an HFD. Male reproductive parameters were evaluated.
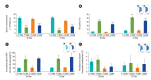
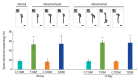
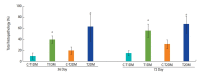
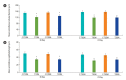
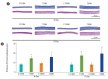
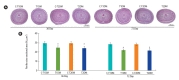
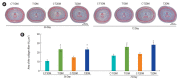
Results: The reproductive organs of the DM mice weighed significantly less than those of controls, and the seminal vesicles plus prostates of the T1DM mice weighed less than those of the T2DM mice. Increased sperm abnormalities and incomplete DNA packaging were observed in the DM groups. Sperm concentration and the proportion of normal sperm were significantly lower in the T1DM group. The seminiferous histopathology of DM mice was classified into seven types. The penises of the DM mice were smaller than those of the controls; however, tunica albuginea thickness and the amount of penile collagen fibers were increased in these mice. Round germ cells were abundant in the epididymal lumens of the mice with DM.
Conclusion: T1DM adversely affected reproductive parameters to a greater extent than T2DM.
Keywords: Mice; Sperm; Streptozotocin; Type 1 diabetes mellitus; Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures



References
-
- Report of the Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Care. 1997;20:1183–97. - PubMed
-
- Frier BM, Fisher M. Diabetes mellitus. In: Colledge NR, Walker BR, Ralston S, Davidson S, editors. Davidson’s principles and practice of medicine. India: Elsevier; 2010. p. 735.
-
- Ahangarpour A, Oroojan AA, Heidari H, Ghaedi E, Taherkhani R. Effects of hydro-alcoholic extract from Arctium lappa L. (Burdock) root on gonadotropins, testosterone, and sperm count and viability in male mice with nicotinamide/streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetes. Malays J Med Sci. 2015;22:25–32. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

