Nanoparticles for treatment of bovine Staphylococcus aureus mastitis
- PMID: 32036717
- PMCID: PMC7034104
- DOI: 10.1080/10717544.2020.1724209
Nanoparticles for treatment of bovine Staphylococcus aureus mastitis
Abstract
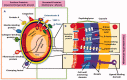
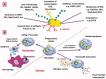
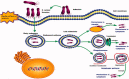
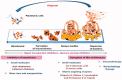
Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) is one of the most important zoonotic bacterial pathogens, infecting human beings and a wide range of animals, in particular, dairy cattle. Globally. S. aureus causing bovine mastitis is one of the biggest problems and an economic burden facing the dairy industry with a strong negative impact on animal welfare, productivity, and food safety. Furthermore, its smart pathogenesis, including facultative intracellular parasitism, increasingly serious antimicrobial resistance, and biofilm formation, make it challenging to be treated by conventional therapy. Therefore, the development of nanoparticles, especially liposomes, polymeric nanoparticles, solid lipid nanoparticles, nanogels, and inorganic nanoparticles, are gaining traction and excellent tools for overcoming the therapeutic difficulty accompanied by S. aureus mastitis. Therefore, in this review, the current progress and challenges of nanoparticles in enhancing the S. aureus mastitis therapy are focused stepwise. Firstly, the S. aureus treatment difficulties by the antimicrobial drugs are analyzed. Secondly, the advantages of nanoparticles in the treatment of S. aureus mastitis, including improving the penetration and accumulation of their payload drugs intracellular, decreasing the antimicrobial resistance, and preventing the biofilm formation, are also summarized. Thirdly, the progression of different types from the nanoparticles for controlling the S. aureus mastitis are provided. Finally, the difficulties that need to be solved, and future prospects of nanoparticles for S. aureus mastitis treatment are highlighted. This review will provide the readers with enough information about the challenges of the nanosystem to help them to design and fabricate more efficient nanoformulations against S. aureus infections.
Keywords: S. aureus; drug delivery; mastitis; nanogel; nanoparticles; resistance.
Figures

References
-
- Alhadrami H, Al-Hazmi F. (2017). Antibacterial activities of titanium oxide nanoparticles. J Bioelectron Nanotechnol 2:5.
-
- Allen TM, Martin FJ. (2004). Advantages of liposomal delivery systems for anthracyclines. Semin Oncol 31:5–15. - PubMed
-
- Arrecubieta C, Lowy FD. (2006). Staphylococcus aureus—eukaryotic cell interactions. In: Fischetti VA, Novick RP, Ferretti JJ, et al., eds. Gram-positive pathogens. 2nd ed. Washington (DC): American Society of Microbiology, 517–25.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
