Epstein-Barr Virus Latent Membrane Protein 1 Regulates Host B Cell MicroRNA-155 and Its Target FOXO3a via PI3K p110α Activation
- PMID: 32038504
- PMCID: PMC6988802
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02692
Epstein-Barr Virus Latent Membrane Protein 1 Regulates Host B Cell MicroRNA-155 and Its Target FOXO3a via PI3K p110α Activation
Abstract
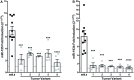
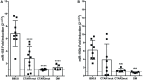
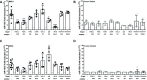
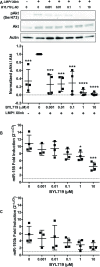
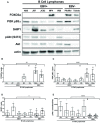
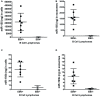
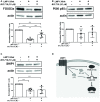
Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) is associated with potentially fatal lymphoproliferations such as post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder (PTLD), a serious complication of transplantation. The viral mechanisms underlying the development and maintenance of EBV+ B cell lymphomas remain elusive but represent attractive therapeutic targets. EBV modulates the expression of host microRNAs (miRs), non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression, to promote survival of EBV+ B cell lymphomas. Here, we examined how the primary oncogene of EBV, latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1), regulates host miRs using an established model of inducible LMP1 signaling. LMP1 derived from the B95.8 lab strain or PTLD induced expression of the oncogene miR-155. However, PTLD variant LMP1 lost the ability to upregulate the tumor suppressor miR-193. Small molecule inhibitors (SMI) of p38 MAPK, NF-κB, and PI3K p110α inhibited upregulation of miR-155 by B95.8 LMP1; no individual SMI significantly reduced upregulation of miR-155 by PTLD variant LMP1. miR-155 was significantly elevated in EBV+ B cell lymphoma cell lines and associated exosomes and inversely correlated with expression of the miR-155 target FOXO3a in cell lines. Finally, LMP1 reduced expression of FOXO3a, which was rescued by a PI3K p110α SMI. Our data indicate that tumor variant LMP1 differentially regulates host B cell miR expression, suggesting viral genotype as an important consideration for the treatment of EBV+ B cell lymphomas. Notably, we demonstrate a novel mechanism in which LMP1 supports the regulation of miR-155 and its target FOXO3a in B cells through activation of PI3K p110α. This mechanism expands on the previously established mechanisms by which LMP1 regulates miR-155 and FOXO3a and may represent both rational therapeutic targets and biomarkers for EBV+ B cell lymphomas.
Keywords: Epstein-Barr virus; FOXO3a; PI3K; latent membrane protein 1; miR-155; microRNA.
Copyright © 2019 Hatton, Smith, Alexander, Mandell, Sherman, Stesney, Hui, Dohrn, Medrano, Ringwalt, Harris-Arnold, Maloney, Krams and Martinez.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Host microRNAs are decreased in pediatric solid-organ transplant recipients during EBV+ Post-transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 7;13:994552. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.994552. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36304469 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus-encoded latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) induces the expression of the cellular microRNA miR-146a.RNA Biol. 2007 Nov;4(3):131-7. doi: 10.4161/rna.4.3.5206. RNA Biol. 2007. PMID: 18347435
-
NF-κB Signaling Regulates Expression of Epstein-Barr Virus BART MicroRNAs and Long Noncoding RNAs in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma.J Virol. 2016 Jun 24;90(14):6475-88. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00613-16. Print 2016 Jul 15. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27147748 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
-
The Latent Membrane Protein 1 (LMP1).Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015;391:119-49. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-22834-1_4. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26428373 Review.
Cited by
-
Activation of MEK1/2/Nrf-2 Signaling Pathway by Epstein-Barr Virus-Latent Membrane Protein 1 Enhances Autophagy and Cisplatin Resistance in T-Cell Lymphoma.Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2021 Jun 18;2021:6668947. doi: 10.1155/2021/6668947. eCollection 2021. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2021. PMID: 34239803 Free PMC article.
-
No small matter: emerging roles for exosomal miRNAs in the immune system.FEBS J. 2022 Jul;289(14):4021-4037. doi: 10.1111/febs.16052. Epub 2021 Jun 19. FEBS J. 2022. PMID: 34087046 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Host microRNAs are decreased in pediatric solid-organ transplant recipients during EBV+ Post-transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 7;13:994552. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.994552. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36304469 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Pathogenic Impact of Cow's Milk Consumption and Bovine Milk-Derived Exosomal MicroRNAs in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 23;24(7):6102. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076102. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37047075 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Virus-Induced Upregulation of the miR-183/96/182 Cluster and the FoxO Family Protein Members Are Not Required for Efficient Replication of HSV-1.Viruses. 2022 Jul 28;14(8):1661. doi: 10.3390/v14081661. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 36016282 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asano N., Yamamoto K., Tamaru J.-I., Oyama T., Ishida F., Ohshima K., et al. . (2009). Age-related Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders: comparison with EBV-positive classic Hodgkin lymphoma in elderly patients. Blood 113, 2629–2636. 10.1182/blood-2008-06-164806, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Beatty P., Krams S., Martinez O. (1997). Involvement of IL-10 in the autonomous growth of EBV-transformed B cell lines. J. Immunol. 158, 4045–4051. PMID: - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

