Left Ventricular Systolic Dysfunction Is a Possible Independent Risk Factor of Radiation Pneumonitis in Locally Advanced Lung Cancer Patients
- PMID: 32039006
- PMCID: PMC6992641
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2019.01511
Left Ventricular Systolic Dysfunction Is a Possible Independent Risk Factor of Radiation Pneumonitis in Locally Advanced Lung Cancer Patients
Abstract
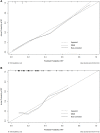
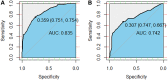
Objectives: To assess the association between left ventricular (LV) systolic and diastolic dysfunction and grade ≥2 radiation pneumonitis (RP) for locally advanced lung cancer patients receiving definitive radiotherapy. Materials and Methods: A retrospective analysis was carried out for 260 lung cancer patients treated with definitive radiotherapy between 2015 and 2017. RP was evaluated according to Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) toxicity criteria. Logistic regression analysis, 10-fold cross validation, and external validation were performed. The prediction model's discriminative performance was evaluated using the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC), and calibration of the model was assessed by the Hosmer-Lemeshow test and the calibration curve. Results: Within the first 6 months after radiotherapy, 70 patients (26.9%) developed grade ≥2 RP. Reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) before radiotherapy was detected in 53 patients (20.4%). The odds ratio (OR) of developing RP for patients with LVEF <50% was 3.42 [p < 0.001, 95% confidence interval (CI), 1.85-6.32]. Multivariate analysis showed that forced expiratory volume in the first second/forced vital capacity (FEV1/FVC), LVEF, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status, chemotherapy, and mean lung dose (MLD) were significantly associated with grade ≥2 RP. The AUC of a model including the above five variables was 0.835 (95% CI, 0.778-0.891) on 10-fold cross validation and 0.742 (95% CI, 0.633-0.851) on the external validation set. The p-value for the Hosmer-Lemeshow test was 0.656 on 10-fold cross validation and 0.534 on the external validation set. Conclusion: LV systolic dysfunction is a possible independent risk factor for RP in locally advanced lung cancer patients receiving definitive radiotherapy.
Keywords: definitive radiotherapy; left ventricular ejection fraction; left ventricular systolic dysfunction; locally advanced lung cancer; radiation pneumonitis.
Copyright © 2020 Cai, Liang, Li, Meng and Yu.
Figures

References
-
- Takada M, Fukuoka M, Kawahara M, Sugiura T, Yokoyama A, Yokota S, et al. Phase III study of concurrent versus sequential thoracic radiotherapy in combination with cisplatin and etoposide for limited-stage small-cell lung cancer: results of the Japan Clinical Oncology Group Study 9104. J Clin Oncol. (2002) 20:3054–60. 10.1200/JCO.2002.12.071 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tsujino K, Hashimoto T, Shimada T, Yoden E, Fujii O, Ota Y, et al. Combined analysis of V20, VS5, pulmonary fibrosis score on baseline computed tomography, and patient age improves prediction of severe radiation pneumonitis after concurrent chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. (2014) 9:983–90. 10.1097/JTO.0000000000000187 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

