Pulmonary artery aneurysm rupture
- PMID: 32039062
- PMCID: PMC6945309
- DOI: 10.4322/acr.2019.131
Pulmonary artery aneurysm rupture
Abstract
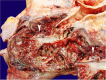
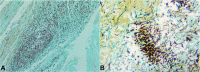
Pulmonary artery aneurysm is a disorder of varying etiology and should be diagnosed early for appropriate interventions. A 45-year-old man was hospitalized for chest pain, dyspnea, cough, chills, diarrhea, and vomiting, which had started 3 weeks before admission. Physical examination indicated a reduced vesicular murmur in the right hemithorax. A chest x-ray performed indicated a pneumothorax and pulmonary abscess in the right hemithorax. Thoracostomy released abundant purulent and fetid fluid. Direct examination of the pleural fluid using saline revealed structures similar to Trichomonas. Non-contrast chest computed tomography revealed right pneumothorax along with an irregular cavitation located at the pleuropulmonary interface of the posterior margin of the right lower lobe. A pleurostomy was performed. On the second postoperative day, the patient suffered a sudden major hemorrhage through the surgical wound and died on the way to the operating room. The autopsy revealed an abscess and ruptured aneurysm of the lower lobar artery in the lower right lung. Microscopic examination revealed extensive liquefactive necrosis associated with purulent inflammation and the presence of filamentous fungi and spores. This case can be characterized as a severe disorder that requires early diagnosis to achieve a good therapeutic response and to avoid fatal outcomes.
Keywords: Aneurysm, Rupture; Hemoptysis; Lung abscess; Thoracotomy; Trichomonas Infections.
Autopsy and Case Reports. ISSN 2236-1960. Copyright © 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: None
Figures





References
-
- Finkbeiner WE, Ursell PC, Davis RL. Autopsy pathology: a manual and atlas. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier; 2009. 10.1016/B978-1-4160-5453-5.00015-X. - DOI
-
- Stedman TL. Stedman’s Medical Dictionary. 27th ed. Baltimore: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2000.

