Comparison between iRoot BP Plus (EndoSequence Root Repair Material) and Mineral Trioxide Aggregate as Pulp-capping Agents: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 32039073
- PMCID: PMC6905310
- DOI: 10.4103/jispcd.JISPCD_249_19
Comparison between iRoot BP Plus (EndoSequence Root Repair Material) and Mineral Trioxide Aggregate as Pulp-capping Agents: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Introduction: iRoot BP Plus, also known as EndoSequence root repair material (EERM) is a premixed bioceramic thick/putty. According to its instruction manual, iRoot BP Plus is composed of tricalcium silicate, zirconium oxide, tantalum pentoxide, dicalcium silicate, calcium sulfate, calcium phosphate monobasic, and filler agents. This systematic review was carried out to evaluate and present the iRoot BP Plus material as a pulp-capping agent.
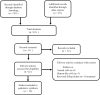
Materials and methods: A systematic search for articles with the scope of the selection criteria undergoing for data extraction was conducted through electronic databases. Studies on evaluation of the cytotoxicity, bioactivity, and dentinal bridge formation of iRoot BP, iRoot BP Plus, ERRM putty, or ERRM paste (ERRM) on variant human cells were selected for in vitro models, and dentinal bridge formation on human and animals teeth for in vivo models were selected.
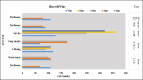
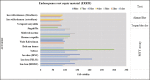
Results: A total of 22 articles were discussed in the review, 14 in vitro studies, five in vivo studies, and three articles with both studies. Methyl thiazol tetrazolium was the most used method for evaluating cytotoxicity. As for dentinal bridge formation, histological assessment and micro-Computed tomography were used. Human dental pulp cells (hDPCs) were the most investigated for in vitro models and rats for in vivo models. Except for one study, all studies involved in this review were primarily examining the material and comparing it to different types of mineral trioxide aggregate.
Conclusion: iRoot BP, iRoot BP Plus, and ERRM are biocompatible materials that enhance hDPCs and other variant human cells proliferation, migration, attachment adhesion, mineralization, and dentinal bridge formation.
Keywords: EndoSequence root repair material; iRoot BP; iRoot BP Plus; pulp capping.
Copyright: © 2019 Journal of International Society of Preventive and Community Dentistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Walton RE, Torabinejad M. Philadelphia, itd: WB Saunders Co; 1996. Principles and Practice of Endodontics; pp. 201–33.
-
- Cohen B, Combe E. Development of new adhesive pulp capping materials. Dental Update. 1994;21:57–62. - PubMed
-
- Wang Z. Bioceramic materials in endodontics. Endodontic Topics. 2015;32:3–30.
-
- Budig CG, Eleazer PD. In vitro comparison of the setting of dry ProRoot MTA by moisture absorbed through the root. J Endodontics. 2008;34:712–4. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials