Bioactive Triterpenoid Saponins From the Seeds of Aesculus chinensis Bge. var. chekiangensis
- PMID: 32039145
- PMCID: PMC6989559
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2019.00908
Bioactive Triterpenoid Saponins From the Seeds of Aesculus chinensis Bge. var. chekiangensis
Abstract
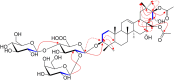
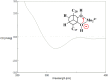
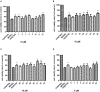
Phytochemical investigation of Aesculus chinensis Bge. var. chekiangensis (Hu et Fang) Fang obtained 33 triterpenoid saponins, including 14 new ones, aesculiside C-P (1-14). The structure elucidations were performed through comprehensive MS, 1D and 2D-NMR analysis, and their absolute configuration was unambiguously determined by X-ray diffraction analysis as well as Mo2(OAc)4-induced ECD method for the first time. All the substances were examined for their cytotoxic activities against three tumor cell lines, Hep G2, HCT-116, and MGC-803. Of these, compounds 8, 9, 14-16, 18, and 22 exhibited potent cytotoxicities against all cell lines with IC50 of 2-21 μM, while compounds 3, 6, 7, 17-19, 20, 24, and 28 depicted moderate activity (IC50 13 to >40 μM). On these bases, the preliminary structure-activity correlations were also discussed. Meanwhile the neuroprotective properties of triterpenoid saponins from Aesculus genus were evaluated for the first time. Among them, compounds 1, 4, 12, 20, 22, 25, 29, and 31 exhibited moderate activities against COCl2-induced PC12 cell injury.
Keywords: Aesculus chinensis Bge. var. chekiangensis (Hu et Fang) Fang; cytotoxic activities; neuroprotective activities; phytochemistry; triterpenoid saponins.
Copyright © 2020 Zhang, Wei, Cao, Zhang, Kang, Ding and Qiu.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Phenylethanol glycosides from the seeds of Aesculus chinensis var. chekiangensis.BMC Chem. 2020 Apr 22;14(1):31. doi: 10.1186/s13065-020-00685-3. eCollection 2020 Dec. BMC Chem. 2020. PMID: 32337510 Free PMC article.
-
New Indole Glycosides from Aesculus chinensis var. chekiangensis and Their Neuroprotective Activities.Molecules. 2019 Nov 9;24(22):4063. doi: 10.3390/molecules24224063. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31717579 Free PMC article.
-
Triterpenoid Saponins from the Seeds of Aesculus chinensis and Their Cytotoxicities.Nat Prod Bioprospect. 2018 Feb;8(1):47-56. doi: 10.1007/s13659-017-0148-4. Epub 2017 Dec 29. Nat Prod Bioprospect. 2018. PMID: 29285602 Free PMC article.
-
Antihyperglycemic effects of triterpenoid saponins from the seeds of Aesculus chinensis Bge.Phytochemistry. 2024 May;221:114049. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2024.114049. Epub 2024 Mar 8. Phytochemistry. 2024. PMID: 38462214
-
Pharmacological activities and molecular mechanisms of Pulsatilla saponins.Chin Med. 2022 May 23;17(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s13020-022-00613-8. Chin Med. 2022. PMID: 35606807 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative Metabolomics of Reproductive Organs in the Genus Aesculus (Sapindaceae) Reveals That Immature Fruits Are a Key Organ of Procyanidin Accumulation and Bioactivity.Plants (Basel). 2021 Dec 8;10(12):2695. doi: 10.3390/plants10122695. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34961166 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the Glucosylation of Astringency Compounds of Horse Chestnut via Integrative Sensory Evaluation, Flavonoid Metabolism, Differential Transcriptome, and Phylogenetic Analysis.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Feb 3;12:830343. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.830343. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35185970 Free PMC article.
-
Phenylethanol glycosides from the seeds of Aesculus chinensis var. chekiangensis.BMC Chem. 2020 Apr 22;14(1):31. doi: 10.1186/s13065-020-00685-3. eCollection 2020 Dec. BMC Chem. 2020. PMID: 32337510 Free PMC article.
-
Medicinal Plants with Potential Inhibitory Bioactive Compounds against Coronaviruses.Adv Pharm Bull. 2022 Jan;12(1):7-16. doi: 10.34172/apb.2022.003. Epub 2021 Jan 30. Adv Pharm Bull. 2022. PMID: 35517886 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential Anti-Inflammatory Constituents from Aesculus wilsonii Seeds.Molecules. 2024 Mar 3;29(5):1136. doi: 10.3390/molecules29051136. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38474647 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

