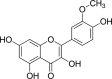
Isorhamnetin inhibited the proliferation and metastasis of androgen-independent prostate cancer cells by targeting the mitochondrion-dependent intrinsic apoptotic and PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway
- PMID: 32039440
- PMCID: PMC7080645
- DOI: 10.1042/BSR20192826
Isorhamnetin inhibited the proliferation and metastasis of androgen-independent prostate cancer cells by targeting the mitochondrion-dependent intrinsic apoptotic and PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway
Abstract
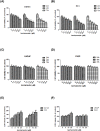
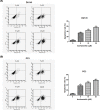
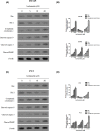
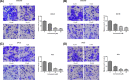
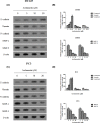
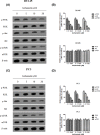
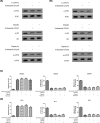
The present study investigated the effects of Isorhamnetin on two types of prostate cancer cells (androgen-independent and androgen-dependent) and explored its possible mechanisms underlying such effects. Treatment with Isorhamnetin significantly inhibited cell growth and induced lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release of androgen-independent DU145 and PC3 prostate cancer cells, but exhibited almost no toxicity effect on androgen-dependent LNCaP prostate cancer cell line or normal human prostate epithelial PrEC cells, which was achieved by the induction of apoptosis in a mitochondrion-dependent intrinsic apoptotic pathway. Furthermore, Isorhamnetin inhibited cell migration and invasion in concentration-dependent manners by enhancing mesenchymal-epithelial transition (MET) and inhibiting matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) 2 (MMP-2) and MMP-9 overexpression. In addition, Isorhamnetin also down-regulated the expression of phosphorylated PI3K (p-P13K), Akt (p-Akt), and mTOR (p-mTOR) proteins in both cancer cells, revealing Isorhamnetin to be a selective PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathway inhibitor. In summary, these findings propose that Isorhamnetin might be a novel therapeutic candidate for the treatment of androgen-independent prostate cancer.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Isorhamnetin; Metastasis; PI3K/Akt/mTOR; Prostate cancer.
© 2020 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Shikonin inhibits prostate cancer cells metastasis by reducing matrix metalloproteinase-2/-9 expression via AKT/mTOR and ROS/ERK1/2 pathways.Int Immunopharmacol. 2014 Aug;21(2):447-55. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2014.05.026. Epub 2014 Jun 3. Int Immunopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24905636
-
mTOR is a fine tuning molecule in CDK inhibitors-induced distinct cell death mechanisms via PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling axis in prostate cancer cells.Apoptosis. 2016 Oct;21(10):1158-78. doi: 10.1007/s10495-016-1275-9. Apoptosis. 2016. PMID: 27484210
-
Signal transduction pathways in androgen-dependent and -independent prostate cancer cell proliferation.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2005 Mar;12(1):119-34. doi: 10.1677/erc.1.00835. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2005. PMID: 15788644
-
The PI3K-AKT-mTOR Pathway and Prostate Cancer: At the Crossroads of AR, MAPK, and WNT Signaling.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 25;21(12):4507. doi: 10.3390/ijms21124507. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32630372 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of PI3K-AKT-mTOR Pathway as a Pro-Survival Signaling and Resistance-Mediating Mechanism to Therapy of Prostate Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 14;22(20):11088. doi: 10.3390/ijms222011088. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34681745 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
From Therapy Resistance to Targeted Therapies in Prostate Cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 May 24;12:877379. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.877379. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35686097 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide (GLP) enhances antitumor immune response by regulating differentiation and inhibition of MDSCs via a CARD9-NF-κB-IDO pathway.Biosci Rep. 2020 Jun 26;40(6):BSR20201170. doi: 10.1042/BSR20201170. Biosci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32530032 Free PMC article.
-
The Involvement of Natural Polyphenols in the Chemoprevention of Cervical Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 16;22(16):8812. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168812. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445518 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential of Kalanchoe pinnata as a Cancer Treatment Adjuvant and an Epigenetic Regulator.Molecules. 2022 Sep 29;27(19):6425. doi: 10.3390/molecules27196425. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36234962 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research progress on antitumor effects of sea buckthorn, a traditional Chinese medicine homologous to food and medicine.Front Nutr. 2024 Jul 9;11:1430768. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1430768. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39045282 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel R., Ward E., Brawley O. and Jemal A. (2011) Cancer statistics, 2011: the impact of eliminating socioeconomic and racial disparities on premature cancer deaths. CA Cancer J. Clin. 61, 212–236 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

