A T-cell-redirecting bispecific G-protein-coupled receptor class 5 member D x CD3 antibody to treat multiple myeloma
- PMID: 32040549
- PMCID: PMC7146017
- DOI: 10.1182/blood.2019003342
A T-cell-redirecting bispecific G-protein-coupled receptor class 5 member D x CD3 antibody to treat multiple myeloma
Abstract
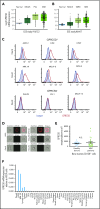
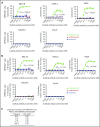
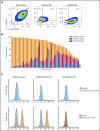
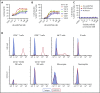
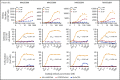
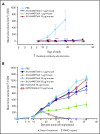
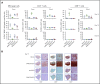
T-cell-mediated approaches have shown promise in myeloma treatment. However, there are currently a limited number of specific myeloma antigens that can be targeted, and multiple myeloma (MM) remains an incurable disease. G-protein-coupled receptor class 5 member D (GPRC5D) is expressed in MM and smoldering MM patient plasma cells. Here, we demonstrate that GPRC5D protein is present on the surface of MM cells and describe JNJ-64407564, a GPRC5DxCD3 bispecific antibody that recruits CD3+ T cells to GPRC5D+ MM cells and induces killing of GPRC5D+ cells. In vitro, JNJ-64407564 induced specific cytotoxicity of GPRC5D+ cells with concomitant T-cell activation and also killed plasma cells in MM patient samples ex vivo. JNJ-64407564 can recruit T cells and induce tumor regression in GPRC5D+ MM murine models, which coincide with T-cell infiltration at the tumor site. This antibody is also able to induce cytotoxicity of patient primary MM cells from bone marrow, which is the natural site of this disease. GPRC5D is a promising surface antigen for MM immunotherapy, and JNJ-64407564 is currently being evaluated in a phase 1 clinical trial in patients with relapsed or refractory MM (NCT03399799).
© 2020 by The American Society of Hematology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: All authors are employees of Janssen Pharmaceuticals and have ownership interest in Johnson & Johnson.
Figures


References
-
- Jagannath S, Roy A, Kish J, et al. Real-world treatment patterns and associated progression-free survival in relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma among US community oncology practices. Expert Rev Hematol. 2016;9(7):707-717. - PubMed
-
- Palumbo A, Anderson K. Multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med. 2011;364(11):1046-1060. - PubMed
-
- Sanford M. Blinatumomab: first global approval. Drugs. 2015;75(3):321-327. - PubMed
-
- Topp MS, Kufer P, Gökbuget N, et al. Targeted therapy with the T-cell-engaging antibody blinatumomab of chemotherapy-refractory minimal residual disease in B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients results in high response rate and prolonged leukemia-free survival. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(18):2493-2498. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

