Genome-wide Identification of Foxf2 Target Genes in Palate Development
- PMID: 32040930
- PMCID: PMC7088206
- DOI: 10.1177/0022034520904018
Genome-wide Identification of Foxf2 Target Genes in Palate Development
Abstract
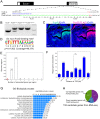
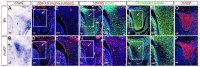
Cleft palate is among the most common structural birth defects in humans. Previous studies have shown that mutations in FOXF2 are associated with cleft palate in humans and mice and that Foxf2 acts in a Shh-Foxf-Fgf18-Shh molecular network controlling palatal shelf growth. In this study, we combined RNA-seq and ChIP-seq approaches to identify direct transcriptional target genes mediating Foxf2 function in palate development in mice. Of 155 genes that exhibited Foxf2-dependent expression in the developing palatal mesenchyme, 88 contained or were located next to Foxf2-binding sites. Through in situ hybridization analyses, we demonstrate that expression of many of these target genes, including multiple genes encoding transcription factors and several encoding extracellular matrix-modifying proteins, were specifically upregulated in the posterior region of palatal shelves in Foxf2-/- mouse embryos. Foxf2 occupancy at many of these putative target loci, including Fgf18, in the developing palatal tissues was verified by ChIP-polymerase chain reaction analyses. One of the Foxf2 target genes, Chst2, encodes a carbohydrate sulfotransferase integral to glycosaminoglycan sulfation. Correlating with ectopic Chst2 expression, Foxf2-/- embryos a exhibited region-specific increase in sulfated keratan sulfate and a concomitant reduction in chondroitin sulfate accumulation in the posterior palatal mesenchyme. However, expression of the core protein of versican, a major chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan important in palatal shelf morphogenesis, was increased, whereas expression of collagen I was reduced in the corresponding region of the palatal mesenchyme. These results indicate that, in addition to regulating palatal shelf growth through the Fgf18-Shh signaling network, Foxf2 controls palatal shelf morphogenesis through regulating expression of multiple transcription factors as well as through directly controlling the synthesis and processing of extracellular matrix components in the palatal mesenchyme. Our ChIP-seq and RNA-seq data sets provide an excellent resource for comprehensive understanding of the molecular network controlling palate development.
Keywords: ChIP-seq; RNA-seq; cleft palate; craniofacial; extracellular matrix; palatogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the authorship and/or publication of this article.
Figures



References
-
- Brinkley LL, Vickerman MM. 1982. The effects of chlorcyclizine-induced alterations of glycosaminoglycans on mouse palatal shelf elevation in vivo and in vitro. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 69:193–213. - PubMed
-
- Chai Y, Maxson RE., Jr. 2006. Recent advances in craniofacial morphogenesis. Dev Dyn. 235(9):2353–2375. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

