Wearable Sensor System to Monitor Physical Activity and the Physiological Effects of Heat Exposure
- PMID: 32041097
- PMCID: PMC7039288
- DOI: 10.3390/s20030855
Wearable Sensor System to Monitor Physical Activity and the Physiological Effects of Heat Exposure
Abstract
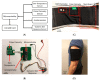
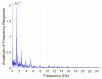
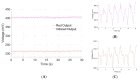
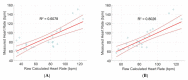
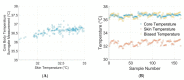
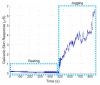
Mobile health monitoring via non-invasive wearable sensors is poised to advance telehealth for older adults and other vulnerable populations. Extreme heat and other environmental conditions raise serious health challenges that warrant monitoring of real-time physiological data as people go about their normal activities. Mobile systems could be beneficial for many communities, including elite athletes, military special forces, and at-home geriatric monitoring. While some commercial monitors exist, they are bulky, require reconfiguration, and do not fit seamlessly as a simple wearable device. We designed, prototyped and tested an integrated sensor platform that records heart rate, oxygen saturation, physical activity levels, skin temperature, and galvanic skin response. The device uses a small microcontroller to integrate the measurements and store data directly on the device for up to 48+ h. continuously. The device was compared to clinical standards for calibration and performance benchmarking. We found that our system compared favorably with clinical measures, such as fingertip pulse oximetry and infrared thermometry, with high accuracy and correlation. Our novel platform would facilitate an individualized approach to care, particularly those whose access to healthcare facilities is limited. The platform also can be used as a research tool to study physiological responses to a variety of environmental conditions, such as extreme heat, and can be customized to incorporate new sensors to explore other lines of inquiry.
Keywords: activity monitoring; galvanometric response; heart rate; personalized medicine; skin temperature; telehealth; wearable physiological sensors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Wearable Ring-Shaped Biomedical Device for Physiological Monitoring through Finger-Based Acquisition of Electrocardiographic, Photoplethysmographic, and Galvanic Skin Response Signals: Design and Preliminary Measurements.Biosensors (Basel). 2024 Apr 20;14(4):205. doi: 10.3390/bios14040205. Biosensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38667198 Free PMC article.
-
Flexible Electronics toward Wearable Sensing.Acc Chem Res. 2019 Mar 19;52(3):523-533. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.8b00500. Epub 2019 Feb 15. Acc Chem Res. 2019. PMID: 30767497 Review.
-
Raw Photoplethysmography as an Enhancement for Research-Grade Wearable Activity Monitors.JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2024 Sep 27;12:e57158. doi: 10.2196/57158. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2024. PMID: 39331461 Free PMC article.
-
Beat the heat: wearable-based study of perceived heat stress and physiological strain in swiss track workers in a controlled climate chamber.Physiol Meas. 2024 Dec 4;45(12). doi: 10.1088/1361-6579/ad9683. Physiol Meas. 2024. PMID: 39580817
-
Wearable physiological monitoring for human thermal-work strain optimization.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2018 Feb 1;124(2):432-441. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00353.2017. Epub 2017 Aug 10. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2018. PMID: 28798200 Review.
Cited by
-
Arousal Detection in Elderly People from Electrodermal Activity Using Musical Stimuli.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Aug 25;20(17):4788. doi: 10.3390/s20174788. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32854302 Free PMC article.
-
Continuous monitoring of body temperature for objective detection of health and safety risks in construction sites: An analysis of the accuracy and comfort of off-the-shelf wearable sensors.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 3;10(6):e26947. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26947. eCollection 2024 Mar 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38545166 Free PMC article.
-
Heart Rate Measurement Using the Built-In Triaxial Accelerometer from a Commercial Digital Writing Device.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Mar 31;24(7):2238. doi: 10.3390/s24072238. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38610449 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Hidden Complexity: Entropy Analysis in Pulse Oximetry of Female Athletes.Biosensors (Basel). 2024 Jan 19;14(1):0. doi: 10.3390/bios14010052. Biosensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38275305 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic and meta-based evaluation of the relationship between the built environment and physical activity behaviors among older adults.PeerJ. 2023 Sep 25;11:e16173. doi: 10.7717/peerj.16173. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 37780389 Free PMC article.

