Urinary Excretion of N1-methyl-2-pyridone-5-carboxamide and N1-methylnicotinamide in Renal Transplant Recipients and Donors
- PMID: 32041099
- PMCID: PMC7074074
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm9020437
Urinary Excretion of N1-methyl-2-pyridone-5-carboxamide and N1-methylnicotinamide in Renal Transplant Recipients and Donors
Abstract
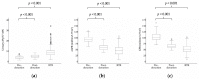
N1-methylnicotinamide (N1-MN) and N1-methyl-2-pyridone-5-carboxamide (2Py) are successive end products of NAD+ catabolism. N1-MN excretion in 24-h urine is the established biomarker of niacin nutritional status, and recently shown to be reduced in renal transplant recipients (RTR). However, it is unclear whether 2Py excretion is increased in this population, and, if so, whether a shift in excretion of N1-MN to 2Py can be attributed to kidney function. Hence, we assessed the 24-h urinary excretion of 2Py and N1-MN in RTR and kidney donors before and after kidney donation, and investigated associations of the urinary ratio of 2Py to N1-MN (2Py/N1-MN) with kidney function, and independent determinants of urinary 2Py/N1-MN in RTR. The urinary excretion of 2Py and N1-MN was measured in a cross-sectional cohort of 660 RTR and 275 healthy kidney donors with liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). Linear regression analyses were used to investigate associations and determinants of urinary 2Py/N1-MN. Median 2Py excretion was 178.1 (130.3-242.8) μmol/day in RTR, compared to 155.6 (119.6-217.6) μmol/day in kidney donors (p < 0.001). In kidney donors, urinary 2Py/N1-MN increased significantly after kidney donation (4.0 ± 1.4 to 5.2 ± 1.5, respectively; p < 0.001). Smoking, alcohol consumption, diabetes, high-density lipoprotein (HDL), high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) were identified as independent determinants of urinary 2Py/N1-MN in RTR. In conclusion, the 24-h urinary excretion of 2Py is higher in RTR than in kidney donors, and urinary 2Py/N1-MN increases after kidney donation. As our data furthermore reveal strong associations of urinary 2Py/N1-MN with kidney function, interpretation of both N1-MN and 2Py excretion may be recommended for assessment of niacin nutritional status in conditions of impaired kidney function.
Keywords: N1-methyl-2-pyridone-5-carboxamide; N1-methylnicotinamide; biomarker; kidney function; niacin status; renal transplantation; tryptophan; urinary excretion; vitamin B3.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Urinary Excretion of N1-Methylnicotinamide and N1-Methyl-2-Pyridone-5-Carboxamide and Mortality in Kidney Transplant Recipients.Nutrients. 2020 Jul 10;12(7):2059. doi: 10.3390/nu12072059. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32664445 Free PMC article.
-
Urinary Excretion of N1-Methylnicotinamide, as a Biomarker of Niacin Status, and Mortality in Renal Transplant Recipients.J Clin Med. 2019 Nov 12;8(11):1948. doi: 10.3390/jcm8111948. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 31726722 Free PMC article.
-
N1-Methylnicotinamide: The Mysterious Anti-aging Actor in Renal Transplantation.Curr Pharm Des. 2023;29(10):723-731. doi: 10.2174/1381612829666230330083649. Curr Pharm Des. 2023. PMID: 37005540
-
N-methyl-2-pyridone-5-carboxamide: a novel uremic toxin?Kidney Int Suppl. 2003 May;(84):S19-21. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.63.s84.36.x. Kidney Int Suppl. 2003. PMID: 12694300 Review.
-
N-methyl-2-pyridone-5-carboxamide (2PY)-Major Metabolite of Nicotinamide: An Update on an Old Uremic Toxin.Toxins (Basel). 2016 Nov 15;8(11):339. doi: 10.3390/toxins8110339. Toxins (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27854278 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolomic profiles of infants classified as sudden infant death syndrome: a case-control analysis.EBioMedicine. 2025 Jan;111:105484. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2024.105484. Epub 2024 Dec 6. EBioMedicine. 2025. PMID: 39644771 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances and Clinical Outcomes of Kidney Transplantation.J Clin Med. 2020 Apr 22;9(4):1193. doi: 10.3390/jcm9041193. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 32331309 Free PMC article.
-
The Biochemical Pathways of Nicotinamide-Derived Pyridones.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 24;22(3):1145. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031145. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33498933 Free PMC article.
-
An Untargeted Metabolomics Approach on Carfilzomib-Induced Nephrotoxicity.Molecules. 2022 Nov 16;27(22):7929. doi: 10.3390/molecules27227929. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36432029 Free PMC article.
-
Defining NAD(P)(H) Catabolism.Nutrients. 2023 Jul 7;15(13):3064. doi: 10.3390/nu15133064. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37447389 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- EFSA NDA Panel Scientific Opinion on Dietary Reference Values for niacin. EFSA J. 2014;12:3759. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2014.3759. - DOI
-
- World Health Organization and United Nations High Commissions for Refugees Pellagra and Its Prevention and Control in Major Emergencies; WHO/NHD/00.10.2000. [(accessed on 26 March 2018)]; Available online: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/66704/WHO_NHD_00.10.pdf?....
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

