Bisphenol A (BPA)-Induced Changes in the Number of Serotonin-Positive Cells in the Mucosal Layer of Porcine Small Intestine-the Preliminary Studies
- PMID: 32041147
- PMCID: PMC7037014
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21031079
Bisphenol A (BPA)-Induced Changes in the Number of Serotonin-Positive Cells in the Mucosal Layer of Porcine Small Intestine-the Preliminary Studies
Abstract
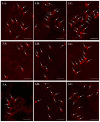
Bisphenol A (BPA) is a substance used in the production of plastics which has a negative impact on many internal organs. Because BPA is normally toxic for the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, the intestine is especially vulnerable to the adverse effects of this substance. The aim of this investigation was to study the influence of two doses of BPA (0.05 mg and 0.5 mg/kg body weight/day) on the number of mucosal cells in the porcine small intestine and containing serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT). During the experiment, it was demonstrated that both applied BPA doses caused an increase in the number of 5-HT-positive cells located in the mucosal layer of the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. These changes may be connected with the direct impact of BPA on the intestinal mucosa, the pro-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties of this substance, and/or the influence of BPA on the neurochemical characterization of nervous structures supplying the intestine.
Keywords: bisphenol A; pig; serotonin; small intestine.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources