Connected Elbow Exoskeleton System for Rehabilitation Training Based on Virtual Reality and Context-Aware
- PMID: 32041156
- PMCID: PMC7038710
- DOI: 10.3390/s20030858
Connected Elbow Exoskeleton System for Rehabilitation Training Based on Virtual Reality and Context-Aware
Abstract
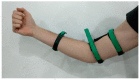
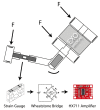
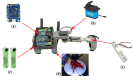
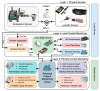
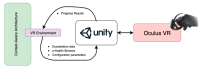
Traditional physiotherapy rehabilitation systems are evolving into more advanced systems based on exoskeleton systems and Virtual Reality (VR) environments that enhance and improve rehabilitation techniques and physical exercise. In addition, due to current connected systems and paradigms such as the Internet of Things (IoT) or Ambient Intelligent (AmI) systems, it is possible to design and develop advanced, effective, and low-cost medical tools that patients may have in their homes. This article presents a low-cost exoskeleton for the elbow that is connected to a Context-Aware architecture and thanks to a VR system the patient can perform rehabilitation exercises in an interactive way. The integration of virtual reality technology in rehabilitation exercises provides an intensive, repetitive and task-oriented capacity to improve patient motivation and reduce work on medical professionals. One of the system highlights is the intelligent ability to generate new exercises, monitor the exercises performed by users in search of progress or possible problems and the dynamic modification of the exercises characteristics. The platform also allows the incorporation of commercial medical sensors capable of collecting valuable information for greater accuracy in the diagnosis and evolution of patients. A case study with real patients with promising results has been carried out.
Keywords: edge computing; elbow rehabilitation; exoskeleton; virtual reality.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Knai C., Brusamento S., Legido-Quigley H., Saliba V., Panteli D., Turk E., Car J., Mckee M., Busse R. Systematic review of the methodological quality of clinical guideline development for the management of chronic disease in Europe. Health Policy. 2012;107:157–167. doi: 10.1016/j.healthpol.2012.06.004. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Huang F.-H. Explore Home Care Needs and Satisfaction for Elderly People with Chronic Disease and their Family Members. Procedia Manuf. 2015;3:173–179. doi: 10.1016/j.promfg.2015.07.123. - DOI
-
- Varshney U. Mobile health: Four emerging themes of research. Decis. Support Syst. 2014;66:20–35. doi: 10.1016/j.dss.2014.06.001. - DOI
-
- Preuveneers D., Berbers Y., Joosen W. The Future of Mobile E-health Application Development: Exploring HTML5 for Context-aware Diabetes Monitoring. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2013;21:351–359. doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2013.09.046. - DOI
-
- Ramos C., Augusto J.C., Shapiro D. Ambient intelligence the next step for artificial intelligence. IEEE Intell. Syst. 2008;23:15–18. doi: 10.1109/MIS.2008.19. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

