Nanocarriers as Magic Bullets in the Treatment of Leukemia
- PMID: 32041219
- PMCID: PMC7075174
- DOI: 10.3390/nano10020276
Nanocarriers as Magic Bullets in the Treatment of Leukemia
Abstract
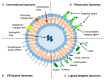
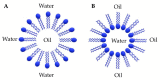
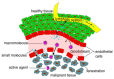
Leukemia is a type of hematopoietic stem/progenitor cell malignancy characterized by the accumulation of immature cells in the blood and bone marrow. Treatment strategies mainly rely on the administration of chemotherapeutic agents, which, unfortunately, are known for their high toxicity and side effects. The concept of targeted therapy as magic bullet was introduced by Paul Erlich about 100 years ago, to inspire new therapies able to tackle the disadvantages of chemotherapeutic agents. Currently, nanoparticles are considered viable options in the treatment of different types of cancer, including leukemia. The main advantages associated with the use of these nanocarriers summarized as follows: i) they may be designed to target leukemic cells selectively; ii) they invariably enhance bioavailability and blood circulation half-life; iii) their mode of action is expected to reduce side effects. FDA approval of many nanocarriers for treatment of relapsed or refractory leukemia and the desired results extend their application in clinics. In the present review, different types of nanocarriers, their capability in targeting leukemic cells, and the latest preclinical and clinical data are discussed.
Keywords: ALL; AML; CLL; CML; leukemia; liposome; nanocarrier; nanoparticle; nanosystem; targeted therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Advanced targeted therapies in cancer: Drug nanocarriers, the future of chemotherapy.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015 Jun;93:52-79. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2015.03.018. Epub 2015 Mar 23. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015. PMID: 25813885 Review.
-
Immunoliposomes in Acute Myeloid Leukaemia Therapy: An Overview of Possible Targets and Obstacles.Curr Med Chem. 2019;26(28):5278-5292. doi: 10.2174/0929867326666190517114450. Curr Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 31099318 Review.
-
Therapeutic targeting of leukemic stem cells in acute myeloid leukemia - the biological background for possible strategies.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2017 Oct;12(10):1053-1065. doi: 10.1080/17460441.2017.1356818. Epub 2017 Jul 27. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2017. PMID: 28748730 Review.
-
Exploring Therapeutic Potential of Nanocarrier Systems Against Breast Cancer.Pharm Nanotechnol. 2018;6(2):94-110. doi: 10.2174/2211738506666180604101920. Pharm Nanotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29866028 Review.
-
Cooperative effect of chidamide and chemotherapeutic drugs induce apoptosis by DNA damage accumulation and repair defects in acute myeloid leukemia stem and progenitor cells.Clin Epigenetics. 2017 Aug 14;9:83. doi: 10.1186/s13148-017-0377-8. eCollection 2017. Clin Epigenetics. 2017. PMID: 28814980 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Characterization of Biological Material Adsorption to the Surface of Nanoparticles without a Prior Separation Step: a Case Study of Glioblastoma-Targeting Peptide and Lipid Nanocapsules.Pharm Res. 2021 Apr;38(4):681-691. doi: 10.1007/s11095-021-03034-8. Epub 2021 Apr 7. Pharm Res. 2021. PMID: 33829340 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of Zr-89-Labeled Folic Acid-Conjugated Silica (SiO2) Microwire as a Tumor Diagnostics Carrier for Positron Emission Tomography.Materials (Basel). 2021 Jun 11;14(12):3226. doi: 10.3390/ma14123226. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34207994 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advance in phytonanomedicine and mineral nanomedicine delivery system of the treatment for acute myeloid leukemia.J Nanobiotechnology. 2023 Jul 26;21(1):240. doi: 10.1186/s12951-023-01968-2. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023. PMID: 37491290 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Computational Frontiers in Aptamer-Based Nanomedicine for Precision Therapeutics: A Comprehensive Review.ACS Omega. 2024 Jun 10;9(25):26838-26862. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c02466. eCollection 2024 Jun 25. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 38947800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stealth-Engineered Albumin-Coated Nanoparticles for Targeted Therapy: Effective Drug Delivery and Tumor Suppression in Xenograft-Zebrafish Model.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Dec 10;19:13267-13286. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S476241. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39679253 Free PMC article.

