Examining the Feasibility and Acceptability of Valuing the Arabic Version of SF-6D in a Lebanese Population
- PMID: 32041284
- PMCID: PMC7038049
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph17031037
Examining the Feasibility and Acceptability of Valuing the Arabic Version of SF-6D in a Lebanese Population
Abstract
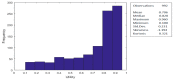
Objectives: The SF-6D is a preference-based measure of health developed to generate utility values from the SF-36. The aim of this pilot study was to examine the feasibility and acceptability of using the standard gamble (SG) technique to generate preference-based values for the Arabic version of SF-6D in a Lebanese population. Methods: The SF-6D was translated into Arabic using forward and backward translations. Forty-nine states defined by the SF-6D were selected using an orthogonal design and grouped into seven sets. A gender-occupation stratified sample of 126 Lebanese adults from the American University of Beirut were recruited to value seven states and the pits using SG. The sample size is appropriate for a pilot study, but smaller than the sample required for a full valuation study. Both interviewers and interviewees reported their understanding and effort levels in the SG tasks. Mean and individual level multivariate regression models were fitted to estimate preference weights for all SF-6D states. The models were compared with those estimated in the UK. Results: Interviewers reported few problems in completing SG tasks (0.8% with a lot of problems) and good respondent understanding (5.6% with little effort and concentration), and 25% of respondents reported the SG task was difficult. A total of 992 SG valuations were useable for econometric modeling. There was no significant change in the test-retest values from 21 subjects. The mean absolute errors in the mean and individual level models were 0.036 and 0.050, respectively, both of which were lower than the UK results. The random effects model adequately predicts the SG values, with the worst state having a value of 0.322 compared to 0.271 in the UK. Conclusion: This pilot confirmed that it was feasible and acceptable to generate preference values with the SG method for the Arabic SF-6D in a Lebanese population. However, further work is needed to extend this to a more representative population, and to explore why no utility values below zero were observed.
Keywords: Lebanese; SF-6D; preference-based measure; reliability; standard gamble; validation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests, except for the copyright to SF-6D held by the University of Sheffield who charge a royalty to commercial users.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Valuation of the SF-6D Health States Is Feasible, Acceptable, Reliable, and Valid in a Chinese Population.Value Health. 2008 Mar-Apr;11(2):295-303. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-4733.2007.00233.x. Value Health. 2008. PMID: 18380642
-
Estimating the SF-6D value set for a population-based sample of Brazilians.Value Health. 2011 Jul-Aug;14(5 Suppl 1):S108-14. doi: 10.1016/j.jval.2011.05.012. Value Health. 2011. PMID: 21839880
-
Estimating the SF-6Dv1 Value Set for a Population-Based Sample in Lebanon.Value Health Reg Issues. 2024 Jul;42:100977. doi: 10.1016/j.vhri.2023.12.008. Epub 2024 Feb 9. Value Health Reg Issues. 2024. PMID: 38340672
-
A Portuguese value set for the SF-6D.Value Health. 2010 Aug;13(5):624-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-4733.2010.00701.x. Epub 2010 Mar 10. Value Health. 2010. PMID: 20230545
-
The Short Form 6 Dimensions (SF-6D): Development and Evolution.Appl Health Econ Health Policy. 2025 Jan;23(1):19-33. doi: 10.1007/s40258-024-00919-8. Epub 2024 Oct 26. Appl Health Econ Health Policy. 2025. PMID: 39460886 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mapping the Minnesota Living with Heart Failure Questionnaire (MLHFQ) to SF-6Dv2 in Chinese patients with heart failure.Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2022 Jun 20;20(1):98. doi: 10.1186/s12955-022-02004-x. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2022. PMID: 35725609 Free PMC article.
-
Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients with Health Conditions in Lebanese Community Setting.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Aug 21;18(16):8817. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18168817. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34444566 Free PMC article.
-
Use of a Non-parametric Bayesian Method to Model Health State Preferences: An Application to Polish and Irish EQ-5D-5L Valuations.Front Public Health. 2022 Jun 23;10:917728. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.917728. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35812518 Free PMC article.
-
Properties of SF-6D when longitudinal data from 16,398 spine surgery procedures is applied to 9 national SF-6D value sets.Acta Orthop. 2021 Oct;92(5):532-537. doi: 10.1080/17453674.2021.1915524. Epub 2021 Apr 23. Acta Orthop. 2021. PMID: 33888046 Free PMC article.
-
Psychometric properties of Arabic-translated-related quality of life scales for people with parkinson disease: a scoping review.BMC Public Health. 2024 Sep 14;24(1):2505. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-20002-0. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39277745 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Drummond M.F., Sculpher M., O’Brien B., Stoddart G.L., Torrance G.W. Oxford Medical Publications. Oxford University Press; Oxford, UK: 2005. Methods for the economic evaluation of health care programs.
-
- National Institute of Health and Care Excellence (NICE) Guide to the Methods of Technology Appraisal 2013. National Institute of Health and Care Excellence (NICE); London, UK: 2013. - PubMed
-
- The Professional Society for Health Economics and Outcomes Research (ISPOR) Pharmacoeconomic Guidelines Around the World. [(accessed on 16 July 2019)];2019 Available online: https://tools.ispor.org/peguidelines/
-
- Brazier J.E., Ratcliffe J., Tsuchiya A., Solomon J. Measuring and Valuing Health for Economic Evaluation. 2nd ed. Oxford University Press; Oxford, UK: 2017.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources