Cytokinins Are Abundant and Widespread Among Insect Species
- PMID: 32041320
- PMCID: PMC7076654
- DOI: 10.3390/plants9020208
Cytokinins Are Abundant and Widespread Among Insect Species
Abstract
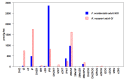
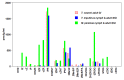
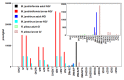
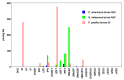
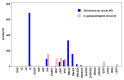
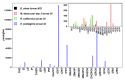
Cytokinins (CKs) are a class of compounds that have long been thought to be exclusively plant growth regulators. Interestingly, some species of phytopathogenic bacteria and fungi have been shown to, and gall-inducing insects have been hypothesized to, produce CKs and use them to manipulate their host plants. We used high performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS/MS) to examine concentrations of a wide range of CKs in 17 species of phytophagous insects, including gall- and non-gall-inducing species from all six orders of Insecta that contain species known to induce galls: Thysanoptera, Hemiptera, Lepidoptera, Coleoptera, Diptera, and Hymenoptera. We found CKs in all six orders of insects, and they were not associated exclusively with gall-inducing species. We detected 24 different CK analytes, varying in their chemical structure and biological activity. Isoprenoid precursor nucleotide and riboside forms of trans-zeatin (tZ) and isopentenyladenine (iP) were most abundant and widespread across the surveyed insect species. Notably, the observed concentrations of CKs often markedly exceeded those reported in plants suggesting that insects are synthesizing CKs rather than obtaining them from the host plant via tissue consumption, compound sequestration, and bioaccumulation. These findings support insect-derived CKs as means for gall-inducing insects to manipulate their host plant to facilitate cell proliferation, and for both gall- and non-gall-inducing insects to modify nutrient flux and plant defenses during herbivory. Furthermore, wide distribution of CKs across phytophagous insects, including non-gall-inducing species, suggests that insect-borne CKs could be involved in manipulation of source-sink mechanisms of nutrient allocation to sustain the feeding site and altering plant defensive responses, rather than solely gall induction. Given the absence of any evidence for genes in the de novo CK biosynthesis pathway in insects, we postulate that the tRNA-ipt pathway is responsible for CK production. However, the unusually high concentrations of CKs in insects, and the tendency toward dominance of their CK profiles by tZ and iP suggest that the tRNA-ipt pathway functions differently and substantially more efficiently in insects than in plants.
Keywords: cytokinins; gall-inducing; insects; non-gall inducing; phytophagous.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

