The selective autophagy receptor SQSTM1/p62 improves lifespan and proteostasis in an evolutionarily conserved manner
- PMID: 32041473
- PMCID: PMC7138197
- DOI: 10.1080/15548627.2020.1725404
The selective autophagy receptor SQSTM1/p62 improves lifespan and proteostasis in an evolutionarily conserved manner
Abstract
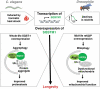
The degradation of specific cargos such as ubiquitinated protein aggregates and dysfunctional mitochondria via macroautophagy/autophagy is facilitated by SQSTM1/p62, the first described selective autophagy receptor in metazoans. While the general process of autophagy plays crucial roles during aging, it remains unclear whether and how selective autophagy mediates effects on longevity and health. Two recent studies in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans and the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster observed gene expression changes of the respective SQSTM1 orthologs in response to environmental stressors or age and showed that overexpression of SQSTM1 is sufficient to extend lifespan and improve proteostasis and mitochondrial function in an autophagy-dependent manner in these model organisms. These findings show that increased expression of the selective autophagy receptor SQSTM1 is sufficient to induce aggrephagy in C. elegans, and mitophagy in Drosophila, and demonstrate an evolutionarily conserved role for SQSTM1 in lifespan determination.
Keywords: Aging; C. elegans; Drosophila; SQST-1; SQSTM1; aggrephagy; heat shock; mitophagy; p62; proteostasis; ref(2)P; selective autophagy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The autophagy receptor p62/SQST-1 promotes proteostasis and longevity in C. elegans by inducing autophagy.Nat Commun. 2019 Dec 11;10(1):5648. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13540-4. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31827090 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of the Autophagy Adaptor p62/SQSTM1 Prolongs Health and Lifespan in Middle-Aged Drosophila.Cell Rep. 2019 Jul 23;28(4):1029-1040.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.06.070. Cell Rep. 2019. PMID: 31340141 Free PMC article.
-
HSF1 stress response pathway regulates autophagy receptor SQSTM1/p62-associated proteostasis.Autophagy. 2017 Jan 2;13(1):133-148. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2016.1248018. Epub 2016 Nov 15. Autophagy. 2017. PMID: 27846364 Free PMC article.
-
Selective Autophagy Receptor p62/SQSTM1, a Pivotal Player in Stress and Aging.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Feb 14;10:793328. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.793328. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35237597 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of selective autophagy: the p62/SQSTM1 paradigm.Essays Biochem. 2017 Dec 12;61(6):609-624. doi: 10.1042/EBC20170035. Print 2017 Dec 12. Essays Biochem. 2017. PMID: 29233872 Review.
Cited by
-
A Crucial Role for the Protein Quality Control System in Motor Neuron Diseases.Front Aging Neurosci. 2020 Jul 21;12:191. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2020.00191. eCollection 2020. Front Aging Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32792938 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagic receptor p62 protects against glycation-derived toxicity and enhances viability.Aging Cell. 2020 Nov;19(11):e13257. doi: 10.1111/acel.13257. Epub 2020 Nov 4. Aging Cell. 2020. PMID: 33146912 Free PMC article.
-
Arginine as host directed therapy in tuberculosis: insights from modulating arginine metabolism by supplementation and arginase inhibition.One Health Adv. 2025;3(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s44280-025-00070-6. Epub 2025 Mar 21. One Health Adv. 2025. PMID: 40124736 Free PMC article.
-
Lysosomal dysfunction-induced autophagic stress in diabetic kidney disease.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Aug;24(15):8276-8290. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15301. Epub 2020 Jun 25. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32583573 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autophagy facilitates age-related cell apoptosis-a new insight from senile cataract.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Jan 10;13(1):37. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-04489-8. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 35013122 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
