Can the low and high b-value distribution influence the pseudodiffusion parameter derived from IVIM DWI in normal brain?
- PMID: 32041549
- PMCID: PMC7011602
- DOI: 10.1186/s12880-020-0419-0
Can the low and high b-value distribution influence the pseudodiffusion parameter derived from IVIM DWI in normal brain?
Abstract
Background: Our study aims to reveal whether the low b-values distribution, high b-values upper limit, and the number of excitation (NEX) influence the accuracy of the intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) parameter derived from multi-b-value diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) in the brain.
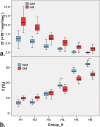
Methods: This prospective study was approved by the local Ethics Committee and informed consent was obtained from each participant. The five consecutive multi-b DWI with different b-value protocols (0-3500 s/mm2) were performed in 22 male healthy volunteers on a 3.0-T MRI system. The IVIM parameters from normal white matter (WM) and gray matter (GM) including slow diffusion coefficient (D), fast perfusion coefficient (D*) and perfusion fraction (f) were compared for differences among defined groups with different IVIM protocols by one-way ANOVA.
Results: The D* and f value of WM or GM in groups with less low b-values distribution (less than or equal to 5 b-values) were significantly lower than ones in any other group with more low b-values distribution (all P < 0.05), but no significant differences among groups with more low b-values distribution (P > 0.05). In addition, no significant differences in the D, D* and f value of WM or GM were found between group with one and more NEX of low b-values distribution (all P > 0.05). IVIM parameters in normal WM and GM strongly depended on the choice of the high b-value upper limit.
Conclusions: Metrics of IVIM parameters can be affected by low and high b value distribution. Eight low b-values distribution with high b-value upper limit of 800-1000 s/mm2 may be the relatively proper set when performing brain IVIM studies.
Keywords: B-value; Brain; Diffusion weighted imaging; Intravoxel incoherent motion; Number of excitation; Pseudodiffusion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Lemke A, Laun FB, Klauss M, Re TJ, Simon D, Delorme S, Schad LR, Stieltjes B. Differentiation of pancreas carcinoma from healthy pancreatic tissue using multiple b-values: comparison of apparent diffusion coefficient and intravoxel incoherent motion derived parameters. Investig Radiol. 2009;44(12):769–775. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0b013e3181b62271. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chandarana H, Kang SK, Wong S, Rusinek H, Zhang JL, Arizono S, Huang WC, Melamed J, Babb JS, Suan EF, et al. Diffusion-weighted intravoxel incoherent motion imaging of renal tumors with histopathologic correlation. Investig Radiol. 2012;47(12):688–696. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0b013e31826a0a49. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

