Five new cases of syndromic intellectual disability due to KAT6A mutations: widening the molecular and clinical spectrum
- PMID: 32041641
- PMCID: PMC7011274
- DOI: 10.1186/s13023-020-1317-9
Five new cases of syndromic intellectual disability due to KAT6A mutations: widening the molecular and clinical spectrum
Abstract
Background: Pathogenic variants of the lysine acetyltransferase 6A or KAT6A gene are associated with a newly identified neurodevelopmental disorder characterized mainly by intellectual disability of variable severity and speech delay, hypotonia, and heart and eye malformations. Although loss of function (LoF) mutations were initially reported as causing this disorder, missense mutations, to date always involving serine residues, have recently been associated with a form of the disorder without cardiac involvement.
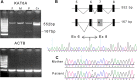
Results: In this study we present five new patients, four with truncating mutations and one with a missense change and the only one not presenting with cardiac anomalies. The missense change [p.(Gly359Ser)], also predicted to affect splicing by in silico tools, was functionally tested in the patient's lymphocyte RNA revealing a splicing effect for this allele that would lead to a frameshift and premature truncation.
Conclusions: An extensive revision of the clinical features of these five patients revealed high concordance with the 80 cases previously reported, including developmental delay with speech delay, feeding difficulties, hypotonia, a high bulbous nose, and recurrent infections. Other features present in some of these five patients, such as cryptorchidism in males, syndactyly, and trigonocephaly, expand the clinical spectrum of this syndrome.
Keywords: Clinical characterization; Clinical genetics; KAT6A; Neurodevelopmental disease; Whole exome sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
KAT6A Syndrome: genotype-phenotype correlation in 76 patients with pathogenic KAT6A variants.Genet Med. 2019 Apr;21(4):850-860. doi: 10.1038/s41436-018-0259-2. Epub 2018 Sep 24. Genet Med. 2019. PMID: 30245513 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of PHF21A causes syndromic intellectual disability with craniofacial anomalies, epilepsy, hypotonia, and neurobehavioral problems including autism.Mol Autism. 2019 Oct 22;10:35. doi: 10.1186/s13229-019-0286-0. eCollection 2019. Mol Autism. 2019. PMID: 31649809 Free PMC article.
-
Phenotypic variability in a family with an inherited KAT6A frameshift variant.Eur J Med Genet. 2025 Feb;73:104993. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2024.104993. Epub 2024 Dec 29. Eur J Med Genet. 2025. PMID: 39740728
-
Comprehensive review and outline of genotypes and phenotypes of Arboleda-Tham syndrome spectrum: insights from novel variants.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Feb 18;52(1):242. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10302-y. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 39964375 Review.
-
Report of a de novo c.2605C > T (p.Pro869Ser) change in the MED13L gene and review of the literature for MED13L-related intellectual disability.Ital J Pediatr. 2020 Jul 9;46(1):95. doi: 10.1186/s13052-020-00847-y. Ital J Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 32646507 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
What Every Internist-Endocrinologist Should Know about Rare Genetic Syndromes in Order to Prevent Needless Diagnostics, Missed Diagnoses and Medical Complications: Five Years of 'Internal Medicine for Rare Genetic Syndromes'.J Clin Med. 2021 Nov 22;10(22):5457. doi: 10.3390/jcm10225457. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34830739 Free PMC article.
-
De Novo PORCN and ZIC2 Mutations in a Highly Consanguineous Family.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 4;22(4):1549. doi: 10.3390/ijms22041549. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33557041 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a novel KAT6A variant in an infant presenting with facial dysmorphism and developmental delay: a case report and literature review.BMC Med Genomics. 2021 Dec 20;14(1):297. doi: 10.1186/s12920-021-01148-x. BMC Med Genomics. 2021. PMID: 34930245 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BRPF1-KAT6A/KAT6B Complex: Molecular Structure, Biological Function and Human Disease.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Aug 23;14(17):4068. doi: 10.3390/cancers14174068. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36077605 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A massive alteration of gene expression in undescended testicles of dogs and the association of KAT6A variants with cryptorchidism.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Feb 13;121(7):e2312724121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2312724121. Epub 2024 Feb 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38315849 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arboleda VA, Lee H, Dorrani N, Zadeh N, Willis M, Macmurdo CF, et al. De novo nonsense mutations in KAT6A, a lysine acetyl-transferase gene, cause a syndrome including microcephaly and global developmental delay. Am J Hum Genet. 2015;96(3):498–506. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2015.01.017. - DOI - PMC - PubMed

