Anabolic response to essential amino acid plus whey protein composition is greater than whey protein alone in young healthy adults
- PMID: 32041644
- PMCID: PMC7011510
- DOI: 10.1186/s12970-020-0340-5
Anabolic response to essential amino acid plus whey protein composition is greater than whey protein alone in young healthy adults
Abstract
Background: We have determined the acute response of protein kinetics to one or two servings (6.3 g and 12.6 g) of a proprietary composition containing free-form essential amino acids (EAA) (3.2 g EAA per serving) and whey protein (2.4 g per serving), as well as the response to consumption of a popular whey-based protein supplement (Gatorade Recover) (17 g; 12.6 g protein).
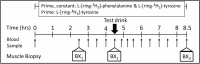
Methods: Whole-body rates of protein synthesis, breakdown and net balance (taken to be the anabolic response) were determined using primed-constant infusions of 2H5-phenylalnine and 2H2-tyrosine. Muscle protein fractional synthetic rate (FSR) was also determined with the 2H5-phenylalanine tracer.
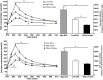
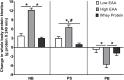
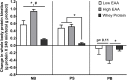
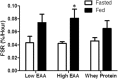
Results: Plasma EAA levels increased following consumption of all beverages, with the greatest response in the high-dose EAA/protein composition. Similarly, the increase in net balance between whole-body protein synthesis and breakdown was greatest following consumption of the high-dose EAA/protein composition, while the low-dose EAA/protein composition and Gatorade Recover induced similar increases in net balance. When the net balance response was normalized for the total amount of product given, the high- and low-dose EAA/protein beverages were approximately 6- and 3-fold more anabolic than the Gatorade Recover, respectively. The greater anabolic response to the EAA/protein composition was due to greater increases in whole-body protein synthesis with both doses, and a markedly greater suppression of whole-body protein breakdown in the high-dose group. Muscle protein FSR after beverage consumption reflected changes in whole-body protein synthesis, with the larger EAA/protein dose significantly increasing FSR.
Conclusion: We conclude that a composition of a balanced EAA formulation combined with whey protein is highly anabolic as compared to a whey protein-based recovery product, and that the response is dose-dependent.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT03502941. This trial was registered on April 19, 2018.
Keywords: Essential amino acids; Fractional synthetic rate; Leucine; Stable isotope; Whey protein; Whole body anabolic response.
Conflict of interest statement
RR Wolfe is the inventor of the pending patent application entitled “Composition for stimulating muscle growth, repair and maintenance”. Remaining authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Muscle Protein Synthesis and Whole-Body Protein Turnover Responses to Ingesting Essential Amino Acids, Intact Protein, and Protein-Containing Mixed Meals with Considerations for Energy Deficit.Nutrients. 2020 Aug 15;12(8):2457. doi: 10.3390/nu12082457. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32824200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Essential amino acid-enriched whey enhances post-exercise whole-body protein balance during energy deficit more than iso-nitrogenous whey or a mixed-macronutrient meal: a randomized, crossover study.J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2021 Jan 7;18(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s12970-020-00401-5. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2021. PMID: 33413462 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Essential Amino Acids and Protein Synthesis: Insights into Maximizing the Muscle and Whole-Body Response to Feeding.Nutrients. 2020 Dec 2;12(12):3717. doi: 10.3390/nu12123717. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 33276485 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of essential amino acid supplementation in stimulating whole body net protein anabolism is comparable between COPD patients and healthy older adults.Metabolism. 2017 Apr;69:120-129. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2016.12.010. Epub 2016 Dec 20. Metabolism. 2017. PMID: 28285641 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A focus on leucine in the nutritional regulation of human skeletal muscle metabolism in ageing, exercise and unloading states.Clin Nutr. 2023 Oct;42(10):1849-1865. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2023.08.010. Epub 2023 Aug 12. Clin Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37625315 Review.
Cited by
-
Essential Amino Acid-Enriched Diet Alleviates Dexamethasone-Induced Loss of Muscle Mass and Function through Stimulation of Myofibrillar Protein Synthesis and Improves Glucose Metabolism in Mice.Metabolites. 2022 Jan 16;12(1):84. doi: 10.3390/metabo12010084. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 35050206 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of amino acid profile in serum of patients with Covid-19 for providing a new treatment strategy.J Med Biochem. 2022 Oct 15;41(4):526-533. doi: 10.5937/jomb0-37514. J Med Biochem. 2022. PMID: 36381071 Free PMC article.
-
Combined Metabolomics and Biochemical Analyses of Serum and Milk Revealed Parity-Related Metabolic Differences in Sanhe Dairy Cattle.Metabolites. 2024 Apr 16;14(4):227. doi: 10.3390/metabo14040227. Metabolites. 2024. PMID: 38668355 Free PMC article.
-
Muscle Protein Synthesis and Whole-Body Protein Turnover Responses to Ingesting Essential Amino Acids, Intact Protein, and Protein-Containing Mixed Meals with Considerations for Energy Deficit.Nutrients. 2020 Aug 15;12(8):2457. doi: 10.3390/nu12082457. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32824200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Cachexia and Fragility in the Patient Candidate for Cardiac Surgery.Nutrients. 2021 Feb 5;13(2):517. doi: 10.3390/nu13020517. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 33562449 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kato H, Volterman KA, West DWD, Suzuki K, Moore DR. Nutritionally non-essential amino acids are dispensable for whole body protein synthesis after exercise in endurance athletes with an adequate essential amio acids intake. Amino Acids. 2018;50(12):1679–1684. doi: 10.1007/s00726-018-2639-y. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Davies Robert W., Bass Joseph J., Carson Brian P., Norton Catherine, Kozior Marta, Amigo-Benavent Miryam, Wilkinson Daniel J., Brook Matthew S., Atherton Philip J., Smith Kenneth, Jakeman Philip M. Differential Stimulation of Post-Exercise Myofibrillar Protein Synthesis in Humans Following Isonitrogenous, Isocaloric Pre-Exercise Feeding. Nutrients. 2019;11(7):1657. doi: 10.3390/nu11071657. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
