Resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: association between preoperative CT texture features and metastatic nodal involvement
- PMID: 32041672
- PMCID: PMC7011565
- DOI: 10.1186/s40644-020-0296-3
Resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: association between preoperative CT texture features and metastatic nodal involvement
Abstract
Background: To explore the relationship between the lymph node status and preoperative computed tomography images texture features in pancreatic cancer.
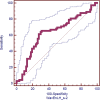
Methods: A total of 155 operable pancreatic cancer patients (104 men, 51 women; mean age 63.8 ± 9.6 years), who had undergone contrast-enhanced computed tomography in the arterial and portal venous phases, were enrolled in this retrospective study. There were 73 patients with lymph node metastases and 82 patients without nodal involvement. Four different data sets, with thin (1.25 mm) and thick (5 mm) slices (at arterial phase and portal venous phase) were analysed. Texture analysis was performed by using MaZda software. A combination of feature selection algorithms was used to determine 30 texture features with the optimal discriminative performance for differentiation between lymph node positive and negative groups. The prediction performance of the selected feature was evaluated by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis.
Results: There were 10 texture features with significant differences between two groups and significance in ROC analysis were identified. They were WavEnLH_s-2(wavelet energy with rows and columns are filtered with low pass and high pass frequency bands with scale factors 2) from wavelet-based features, 135dr_LngREmph (long run emphasis in 135 direction) and 135dr_Fraction (fraction of image in runs in 135 direction) from run length matrix-based features, and seven variables of sum average from coocurrence matrix-based features (SumAverg). The ideal cutoff value for predicting lymph node metastases was 270 for WavEnLH_s-2 (positive likelihood ratio 2.08). In addition, 135dr_LngREmph and 135dr_Fraction were correlated with the ratio of metastatic to examined lymph nodes.
Conclusions: Preoperative computed tomography high order texture features provide a useful imaging signature for the prediction of nodal involvement in pancreatic cancer.
Keywords: Computed tomography; Computer-assisted image processing; Metastases; Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; Texture analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The preoperative prediction of lymph node metastasis of resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma using dual-layer spectral computed tomography.Eur Radiol. 2025 May;35(5):2692-2701. doi: 10.1007/s00330-024-11143-2. Epub 2024 Oct 24. Eur Radiol. 2025. PMID: 39448418
-
Contrast-enhanced CT radiomics for predicting lymph node metastasis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: a pilot study.Cancer Imaging. 2020 Jan 30;20(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s40644-020-0288-3. Cancer Imaging. 2020. PMID: 32000852 Free PMC article.
-
Applying a radiomics-based strategy to preoperatively predict lymph node metastasis in the resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.J Xray Sci Technol. 2020;28(6):1113-1121. doi: 10.3233/XST-200730. J Xray Sci Technol. 2020. PMID: 33074215
-
[Computerized tomography of pancreatic tumors].Tumori. 1999 Jan-Feb;85(1 Suppl 1):S3-5. Tumori. 1999. PMID: 10235071 Review. Italian.
-
Staging of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma with spiral CT and MRI.Rays. 2001 Apr-Jun;26(2):151-9. Rays. 2001. PMID: 11925786 Review.
Cited by
-
Artificial Intelligence Applied to Pancreatic Imaging: A Narrative Review.Healthcare (Basel). 2022 Aug 11;10(8):1511. doi: 10.3390/healthcare10081511. Healthcare (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36011168 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiomic features based on pyradiomics predict CD276 expression associated with breast cancer prognosis.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 3;10(17):e37345. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37345. eCollection 2024 Sep 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39296227 Free PMC article.
-
Contrast-enhanced CT radiomics combined with multiple machine learning algorithms for preoperative identification of lymph node metastasis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Front Oncol. 2024 Sep 13;14:1342317. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1342317. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39346735 Free PMC article.
-
Pancreatic cancer, radiomics and artificial intelligence.Br J Radiol. 2022 Sep 1;95(1137):20220072. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20220072. Epub 2022 Jun 28. Br J Radiol. 2022. PMID: 35687700 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of the value of enhanced CT combined with texture analysis in the differential diagnosis of pulmonary sclerosing pneumocytoma and atypical peripheral lung cancer: a feasibility study.BMC Med Imaging. 2022 Feb 2;22(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s12880-022-00745-1. BMC Med Imaging. 2022. PMID: 35105314 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gilabert M, Boher JM, Raoul JL, Paye F, Bachellier P, Turrini O, et al. Comparison of preoperative imaging and pathological findings for pancreatic head adenocarcinoma: a retrospective analysis by the association Francaise de Chirurgie. Medicine (Baltimore) 2017;96(24):e7214. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000007214. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

