Epigenetic silencing of IGFBPL1 promotes esophageal cancer growth by activating PI3K-AKT signaling
- PMID: 32041673
- PMCID: PMC7011530
- DOI: 10.1186/s13148-020-0815-x
Epigenetic silencing of IGFBPL1 promotes esophageal cancer growth by activating PI3K-AKT signaling
Abstract
Background: There are seven insulin-like growth factor binding proteins (IGFBPs) that bind insulin-like growth factors (IGFs). IGFBP like protein1 (IGFBPL1) is a new member of this family. The function and mechanism of IGFBPL1 in esophageal cancer remains to be elucidated.
Methods: Eight esophageal cancer cell lines, 114 cases of esophageal dysplasia, and 501 cases of primary esophageal cancer samples were examined in this study. Methylation-specific polymerase chain reaction (MSP), immunohistochemistry, Western blot, flow cytometry, RNA interference assay, and xenograft mouse models were employed.
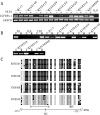
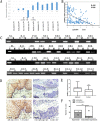
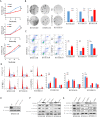
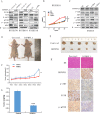
Results: The expression of IGFBPL1was lost and complete methylation was found in KYSE150 and KYSE410 cells. Reduced expression and partial methylation of IGFBPL1 was found in Bic1, KYSE140, KYSE450, KYSE520, and COLO680N cells. High expression and unmethylation was detected in KYSE510 cells. Restoration of IGFBPL1 expression was found in KYSE150 and KYSE410 cells and the expression of IGFBPL1 was increased in Bic1, KYSE140, KYSE450, KYSE520, and COLO680N cells, after 5-AZA-2'-deoxycytidine treatment. IGFBPL1 was methylated in 47.3% (53/114) of esophageal dysplasia and 49.1% (246/501) of human primary esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). Methylation of IGFBPL1 was significantly associated with TNM stage (p = 0.012), and tumor size (p = 0.009). IGFBPL1 inhibited esophageal cancer cell clonal formation and proliferation and induced cell apoptosis and G1/S phase arrest. Further study found that IGFBPL1 is involved in PI3K-AKT signaling and IGFBPL1 suppressed human ESCC xenografts growth in mice.
Conclusion: IGFBPL1 suppresses esophageal cancer cell growth by inhibiting PI3K-AKT signaling in vitro and in vivo. IGFBPL1 is a novel tumor suppressor in human esophageal cancer.
Keywords: DNA methylation; Esophageal cancer; IGFBPL1; PI3K-AKT.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epigenetic silencing of JAM3 promotes esophageal cancer development by activating Wnt signaling.Clin Epigenetics. 2022 Dec 2;14(1):164. doi: 10.1186/s13148-022-01388-3. Clin Epigenetics. 2022. PMID: 36461092 Free PMC article.
-
Methylation of NRN1 is a novel synthetic lethal marker of PI3K-Akt-mTOR and ATR inhibitors in esophageal cancer.Cancer Sci. 2021 Jul;112(7):2870-2883. doi: 10.1111/cas.14917. Epub 2021 May 16. Cancer Sci. 2021. PMID: 33931924 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic silencing of TMEM176A promotes esophageal squamous cell cancer development.Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 25;8(41):70035-70048. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.19550. eCollection 2017 Sep 19. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29050260 Free PMC article.
-
Gene methylation in gastric cancer.Clin Chim Acta. 2013 Sep 23;424:53-65. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2013.05.002. Epub 2013 May 10. Clin Chim Acta. 2013. PMID: 23669186 Review.
-
Targeting epigenetic deregulations for the management of esophageal carcinoma: recent advances and emerging approaches.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2023 Dec;39(6):2437-2465. doi: 10.1007/s10565-023-09818-5. Epub 2023 Jun 20. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 37338772 Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic silencing ZSCAN23 promotes pancreatic cancer growth by activating Wnt signaling.Cancer Biol Ther. 2024 Dec 31;25(1):2302924. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2024.2302924. Epub 2024 Jan 16. Cancer Biol Ther. 2024. PMID: 38226836 Free PMC article.
-
A bioinformatic study of IGFBPs in glioma regarding their diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic prediction value.Am J Transl Res. 2023 Mar 15;15(3):2140-2155. eCollection 2023. Am J Transl Res. 2023. PMID: 37056850 Free PMC article.
-
METTL3/IGF2BP2 Promotes the Malignant Progression of Esophageal Cancer by Activating the PIK3CA/AKT Pathway.Thorac Cancer. 2025 Feb;16(4):e70022. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.70022. Thorac Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39980152 Free PMC article.
-
Expression characteristics and their functional role of IGFBP gene family in pan-cancer.BMC Cancer. 2023 Apr 24;23(1):371. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-10832-3. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37088808 Free PMC article.
-
Absence of genetic association between insulin-like growth factors and esophageal cancer.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Dec 27;103(52):e40899. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000040899. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39969361 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brock MV, Gou M, Akiyama Y, Muller A, Wu TT, Montgomery E, Deasel M, Germonpre P, Rubinson L, Heitmiller RF, et al. Prognostic importance of promoter hypermethylation of multiple genes in esophageal adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9(8):2912–2919. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

