The Development of a Practical Artificial Intelligence Tool for Diagnosing and Evaluating Autism Spectrum Disorder: Multicenter Study
- PMID: 32041690
- PMCID: PMC7244998
- DOI: 10.2196/15767
The Development of a Practical Artificial Intelligence Tool for Diagnosing and Evaluating Autism Spectrum Disorder: Multicenter Study
Abstract
Background: Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental disorder with an unknown etiology. Early diagnosis and intervention are key to improving outcomes for patients with ASD. Structural magnetic resonance imaging (sMRI) has been widely used in clinics to facilitate the diagnosis of brain diseases such as brain tumors. However, sMRI is less frequently used to investigate neurological and psychiatric disorders, such as ASD, owing to the subtle, if any, anatomical changes of the brain.
Objective: This study aimed to investigate the possibility of identifying structural patterns in the brain of patients with ASD as potential biomarkers in the diagnosis and evaluation of ASD in clinics.
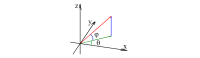
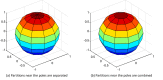
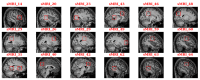
Methods: We developed a novel 2-level histogram-based morphometry (HBM) classification framework in which an algorithm based on a 3D version of the histogram of oriented gradients (HOG) was used to extract features from sMRI data. We applied this framework to distinguish patients with ASD from healthy controls using 4 datasets from the second edition of the Autism Brain Imaging Data Exchange, including the ETH Zürich (ETH), NYU Langone Medical Center: Sample 1, Oregon Health and Science University, and Stanford University (SU) sites. We used a stratified 10-fold cross-validation method to evaluate the model performance, and we applied the Naive Bayes approach to identify the predictive ASD-related brain regions based on classification contributions of each HOG feature.
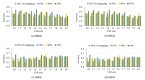
Results: On the basis of the 3D HOG feature extraction method, our proposed HBM framework achieved an area under the curve (AUC) of >0.75 in each dataset, with the highest AUC of 0.849 in the ETH site. We compared the 3D HOG algorithm with the original 2D HOG algorithm, which showed an accuracy improvement of >4% in each dataset, with the highest improvement of 14% (6/42) in the SU site. A comparison of the 3D HOG algorithm with the scale-invariant feature transform algorithm showed an AUC improvement of >18% in each dataset. Furthermore, we identified ASD-related brain regions based on the sMRI images. Some of these regions (eg, frontal gyrus, temporal gyrus, cingulate gyrus, postcentral gyrus, precuneus, caudate, and hippocampus) are known to be implicated in ASD in prior neuroimaging literature. We also identified less well-known regions that may play unrecognized roles in ASD and be worth further investigation.
Conclusions: Our research suggested that it is possible to identify neuroimaging biomarkers that can distinguish patients with ASD from healthy controls based on the more cost-effective sMRI images of the brain. We also demonstrated the potential of applying data-driven artificial intelligence technology in the clinical setting of neurological and psychiatric disorders, which usually harbor subtle anatomical changes in the brain that are often invisible to the human eye.
Keywords: autism spectrum disorder; brain; classification; cluster analysis; histogram of oriented gradients; machine learning; magnetic resonance imaging; neuroimaging.
©Tao Chen, Ye Chen, Mengxue Yuan, Mark Gerstein, Tingyu Li, Huiying Liang, Tanya Froehlich, Long Lu. Originally published in JMIR Medical Informatics (http://medinform.jmir.org), 08.05.2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures


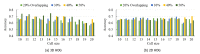
References
-
- Liptak GS, Benzoni LB, Mruzek DW, Nolan KW, Thingvoll MA, Wade CM, Fryer GE. Disparities in diagnosis and access to health services for children with autism: data from the National Survey of Children's Health. J Dev Behav Pediatr. 2008 Jun;29(3):152–60. doi: 10.1097/DBP.0b013e318165c7a0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kentrou V, de Veld DM, Mataw KJ, Begeer S. Delayed autism spectrum disorder recognition in children and adolescents previously diagnosed with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Autism. 2019 May;23(4):1065–72. doi: 10.1177/1362361318785171. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/30244604 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

