Corticotropin-Releasing Factor Receptor-1 Neurons in the Lateral Amygdala Display Selective Sensitivity to Acute and Chronic Ethanol Exposure
- PMID: 32041742
- PMCID: PMC7059189
- DOI: 10.1523/ENEURO.0420-19.2020
Corticotropin-Releasing Factor Receptor-1 Neurons in the Lateral Amygdala Display Selective Sensitivity to Acute and Chronic Ethanol Exposure
Abstract
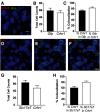
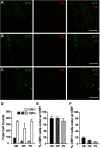
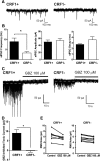
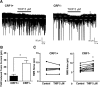
The lateral amygdala (LA) serves as the point of entry for sensory information within the amygdala complex, a structure that plays a critical role in emotional processes and has been implicated in alcohol use disorders. Within the amygdala, the corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) system has been shown to mediate some of the effects of both stress and ethanol, but the effects of ethanol on specific CRF1 receptor circuits in the amygdala have not been fully established. We used male CRF1:GFP reporter mice to characterize CRF1-expressing (CRF1+) and nonexpressing (CRF1-) LA neurons and investigate the effects of acute and chronic ethanol exposure on these populations. The CRF1+ population was found to be composed predominantly of glutamatergic projection neurons with a minority subpopulation of interneurons. CRF1+ neurons exhibited a tonic conductance that was insensitive to acute ethanol. CRF1- neurons did not display a basal tonic conductance, but the application of acute ethanol induced a δ GABAA receptor subunit-dependent tonic conductance and enhanced phasic GABA release onto these cells. Chronic ethanol increased CRF1+ neuronal excitability but did not significantly alter phasic or tonic GABA signaling in either CRF1+ or CRF1- cells. Chronic ethanol and withdrawal also did not alter basal extracellular GABA or glutamate transmitter levels in the LA/BLA and did not alter the sensitivity of GABA or glutamate to acute ethanol-induced increases in transmitter release. Together, these results provide the first characterization of the CRF1+ population of LA neurons and suggest mechanisms for differential acute ethanol sensitivity within this region.
Keywords: CRF; CRF1 receptor; GABA; alcohol; basolateral amygdala; lateral amygdala.
Copyright © 2020 Agoglia et al.
Figures






Similar articles
-
A Functional Switch in Tonic GABA Currents Alters the Output of Central Amygdala Corticotropin Releasing Factor Receptor-1 Neurons Following Chronic Ethanol Exposure.J Neurosci. 2016 Oct 19;36(42):10729-10741. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1267-16.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27798128 Free PMC article.
-
Sex differences in corticotropin releasing factor peptide regulation of inhibitory control and excitability in central amygdala corticotropin releasing factor receptor 1-neurons.Neuropharmacology. 2020 Dec 1;180:108296. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.108296. Epub 2020 Sep 17. Neuropharmacology. 2020. PMID: 32950560 Free PMC article.
-
Presynaptic CRF1 receptors mediate the ethanol enhancement of GABAergic transmission in the mouse central amygdala.ScientificWorldJournal. 2009 Jan 18;9:68-85. doi: 10.1100/tsw.2009.1. ScientificWorldJournal. 2009. PMID: 19151899 Free PMC article.
-
The center of the emotional universe: Alcohol, stress, and CRF1 amygdala circuitry.Alcohol. 2018 Nov;72:61-73. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2018.03.009. Epub 2018 Mar 30. Alcohol. 2018. PMID: 30220589 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ethanol and corticotropin releasing factor receptor modulation of central amygdala neurocircuitry: An update and future directions.Alcohol. 2015 May;49(3):179-84. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2015.01.006. Epub 2015 Jan 29. Alcohol. 2015. PMID: 25716197 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ethanol withdrawal-induced adaptations in prefrontal corticotropin releasing factor receptor 1-expressing neurons regulate anxiety and conditioned rewarding effects of ethanol.Mol Psychiatry. 2022 Aug;27(8):3441-3451. doi: 10.1038/s41380-022-01642-3. Epub 2022 Jun 6. Mol Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35668157 Free PMC article.
-
Alcohol dependence promotes systemic IFN-γ and IL-17 responses in mice.PLoS One. 2020 Dec 21;15(12):e0239246. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0239246. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33347446 Free PMC article.
-
Acute stress activates basolateral amygdala neurons expressing corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor type 1 (CRHR1): Topographical distribution and projection-specific activation in male and female rats.Neurobiol Stress. 2024 Nov 15;33:100694. doi: 10.1016/j.ynstr.2024.100694. eCollection 2024 Nov. Neurobiol Stress. 2024. PMID: 39634490 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting IL-6 as a novel therapeutic approach for alcohol abstinence - related mechanical allodynia.Neuropharmacology. 2025 Nov 1;278:110584. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2025.110584. Epub 2025 Jun 28. Neuropharmacology. 2025. PMID: 40588184
-
Corticotropin releasing factor and drug seeking in substance use disorders: Preclinical evidence and translational limitations.Addict Neurosci. 2022 Dec;4:100038. doi: 10.1016/j.addicn.2022.100038. Epub 2022 Oct 1. Addict Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36531188 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R00 AA025393/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AA013498/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA016985/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AA007573/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AA007456/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA017447/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 NS007431/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K99 AA023002/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P60 AA006420/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA015566/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA021491/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- F32 AA024952/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- K99 AA025393/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA027700/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R00 AA023002/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA026685/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P60 AA011605/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
