Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR drives EZH2-dependent myofibroblast activation in systemic sclerosis through miRNA 34a-dependent activation of NOTCH
- PMID: 32041748
- PMCID: PMC7147169
- DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-216542
Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR drives EZH2-dependent myofibroblast activation in systemic sclerosis through miRNA 34a-dependent activation of NOTCH
Abstract
Background: Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is characterised by autoimmune activation, tissue and vascular fibrosis in the skin and internal organs. Tissue fibrosis is driven by myofibroblasts, that are known to maintain their phenotype in vitro, which is associated with epigenetically driven trimethylation of lysine 27 of histone 3 (H3K27me3).
Methods: Full-thickness skin biopsies were surgically obtained from the forearms of 12 adult patients with SSc of recent onset. Fibroblasts were isolated and cultured in monolayers and protein and RNA extracted. HOX transcript antisense RNA (HOTAIR) was expressed in healthy dermal fibroblasts by lentiviral induction employing a vector containing the specific sequence. Gamma secretase inhibitors were employed to block Notch signalling. Enhancer of zeste 2 (EZH2) was blocked with GSK126 inhibitor.
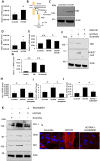
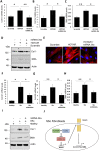
Results: SSc myofibroblasts in vitro and SSc skin biopsies in vivo display high levels of HOTAIR, a scaffold long non-coding RNA known to direct the histone methyltransferase EZH2 to induce H3K27me3 in specific target genes. Overexpression of HOTAIR in dermal fibroblasts induced EZH2-dependent increase in collagen and α-SMA expression in vitro, as well as repression of miRNA-34A expression and consequent NOTCH pathway activation. Consistent with these findings, we show that SSc dermal fibroblast display decreased levels of miRNA-34a in vitro. Further, EZH2 inhibition rescued miRNA-34a levels and mitigated the profibrotic phenotype of both SSc and HOTAIR overexpressing fibroblasts in vitro.
Conclusions: Our data indicate that the EZH2-dependent epigenetic phenotype of myofibroblasts is driven by HOTAIR and is linked to miRNA-34a repression-dependent activation of NOTCH signalling.
Keywords: autoimmune diseases; fibroblasts; systemic sclerosis.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2020. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: H.Y.C. is a co-founder of Accent Therapeutics, Boundless Bio, and advisor to 10x Genomics, Arsenal Biosciences, and Spring Discovery.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR induces GLI2 expression through Notch signalling in systemic sclerosis dermal fibroblasts.Arthritis Res Ther. 2020 Dec 10;22(1):286. doi: 10.1186/s13075-020-02376-9. Arthritis Res Ther. 2020. PMID: 33303026 Free PMC article.
-
Notch signalling regulates fibroblast activation and collagen release in systemic sclerosis.Ann Rheum Dis. 2011 Jul;70(7):1304-10. doi: 10.1136/ard.2010.134742. Epub 2011 Mar 30. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011. PMID: 21450749
-
Lysine Demethylase 1 Has Demethylase-Dependent and Non-Canonical Functions in Myofibroblast Activation in Systemic Sclerosis.Cells. 2025 Mar 14;14(6):433. doi: 10.3390/cells14060433. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40136682 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic factors as drivers of fibrosis in systemic sclerosis.Epigenomics. 2017 Apr;9(4):463-477. doi: 10.2217/epi-2016-0150. Epub 2017 Mar 27. Epigenomics. 2017. PMID: 28343418 Review.
-
Morphogen pathways as molecular targets for the treatment of fibrosis in systemic sclerosis.Arch Dermatol Res. 2013 Jan;305(1):1-8. doi: 10.1007/s00403-012-1304-7. Epub 2012 Dec 4. Arch Dermatol Res. 2013. PMID: 23208311 Review.
Cited by
-
Natural products and long non-coding RNAs in prostate cancer: insights into etiology and treatment resistance.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Jun;398(6):6349-6368. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03736-x. Epub 2025 Jan 18. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39825964 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA networks in circulating exosomes as potential biomarkers for systemic sclerosis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Feb 16;10:1111812. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1111812. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36873898 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Modifications in the Pathogenesis of Systemic Sclerosis.Int J Gen Med. 2022 Mar 19;15:3155-3166. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S356877. eCollection 2022. Int J Gen Med. 2022. PMID: 35342304 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prediction of a Competing Endogenous RNA Co-expression Network by Comprehensive Methods in Systemic Sclerosis-Related Interstitial Lung Disease.Front Genet. 2021 Jul 5;12:633059. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.633059. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34290731 Free PMC article.
-
Noncoding RNAs: Master Regulator of Fibroblast to Myofibroblast Transition in Fibrosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 16;24(2):1801. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021801. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36675315 Free PMC article. Review.

