Fasting-induced FGF21 signaling activates hepatic autophagy and lipid degradation via JMJD3 histone demethylase
- PMID: 32042044
- PMCID: PMC7010817
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-14384-z
Fasting-induced FGF21 signaling activates hepatic autophagy and lipid degradation via JMJD3 histone demethylase
Abstract
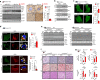
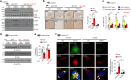
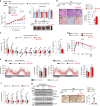
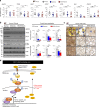
Autophagy is essential for cellular survival and energy homeostasis under nutrient deprivation. Despite the emerging importance of nuclear events in autophagy regulation, epigenetic control of autophagy gene transcription remains unclear. Here, we report fasting-induced Fibroblast Growth Factor-21 (FGF21) signaling activates hepatic autophagy and lipid degradation via Jumonji-D3 (JMJD3/KDM6B) histone demethylase. Upon FGF21 signaling, JMJD3 epigenetically upregulates global autophagy-network genes, including Tfeb, Atg7, Atgl, and Fgf21, through demethylation of histone H3K27-me3, resulting in autophagy-mediated lipid degradation. Mechanistically, phosphorylation of JMJD3 at Thr-1044 by FGF21 signal-activated PKA increases its nuclear localization and interaction with the nuclear receptor PPARα to transcriptionally activate autophagy. Administration of FGF21 in obese mice improves defective autophagy and hepatosteatosis in a JMJD3-dependent manner. Remarkably, in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients, hepatic expression of JMJD3, ATG7, LC3, and ULK1 is substantially decreased. These findings demonstrate that FGF21-JMJD3 signaling epigenetically links nutrient deprivation with hepatic autophagy and lipid degradation in mammals.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Fasting-induced JMJD3 histone demethylase epigenetically activates mitochondrial fatty acid β-oxidation.J Clin Invest. 2018 Jul 2;128(7):3144-3159. doi: 10.1172/JCI97736. Epub 2018 Jun 18. J Clin Invest. 2018. PMID: 29911994 Free PMC article.
-
Liver-enriched transcription factor CREBH interacts with peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α to regulate metabolic hormone FGF21.Endocrinology. 2014 Mar;155(3):769-82. doi: 10.1210/en.2013-1490. Epub 2014 Jan 1. Endocrinology. 2014. PMID: 24424044 Free PMC article.
-
PPARalpha is a key regulator of hepatic FGF21.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007 Aug 24;360(2):437-40. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.06.068. Epub 2007 Jun 21. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007. PMID: 17601491
-
Histone demethylase Jumonji D3 (JMJD3/KDM6B) at the nexus of epigenetic regulation of inflammation and the aging process.J Mol Med (Berl). 2014 Oct;92(10):1035-43. doi: 10.1007/s00109-014-1182-x. Epub 2014 Jun 14. J Mol Med (Berl). 2014. PMID: 24925089 Review.
-
JMJD3 as an epigenetic regulator in development and disease.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2015 Oct;67:148-57. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2015.07.006. Epub 2015 Jul 17. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 26193001 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolic Messengers: FGF21.Nat Metab. 2021 Mar;3(3):309-317. doi: 10.1038/s42255-021-00354-2. Epub 2021 Mar 18. Nat Metab. 2021. PMID: 33758421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrative analysis of the transcriptome and metabolome reveals the importance of hepatokine FGF21 in liver aging.Genes Dis. 2023 Nov 7;11(5):101161. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2023.101161. eCollection 2024 Sep. Genes Dis. 2023. PMID: 39022127 Free PMC article.
-
The FMRFamide Neuropeptide FLP-20 Acts as a Systemic Signal for Starvation Responses in Caenorhabditis elegans.Mol Cells. 2021 Jul 31;44(7):529-537. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2021.0051. Mol Cells. 2021. PMID: 34140426 Free PMC article.
-
Mangiferin Ameliorates Obesity-Associated Inflammation and Autophagy in High-Fat-Diet-Fed Mice: In Silico and In Vivo Approaches.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 5;23(23):15329. doi: 10.3390/ijms232315329. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36499655 Free PMC article.
-
Short Term Isocaloric Ketogenic Diet Modulates NLRP3 Inflammasome Via B-hydroxybutyrate and Fibroblast Growth Factor 21.Front Immunol. 2022 Apr 28;13:843520. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.843520. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35572519 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

