Genetic Analysis of Agronomic Traits and Grain Iron and Zinc Concentrations in a Doubled Haploid Population of Rice (Oryza sativa L.)
- PMID: 32042046
- PMCID: PMC7010768
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-59184-z
Genetic Analysis of Agronomic Traits and Grain Iron and Zinc Concentrations in a Doubled Haploid Population of Rice (Oryza sativa L.)
Abstract
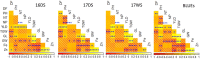
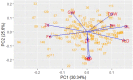
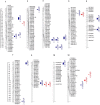
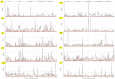
The development of micronutrient dense rice varieties with good agronomic traits is one of the sustainable and cost-effective approaches for reducing malnutrition. Identification of QTLs for high grain Fe and Zn, yield and yield components helps in precise and faster development of high Fe and Zn rice. We carried out a three-season evaluation using IR05F102 x IR69428 derived doubled-haploid population at IRRI. Inclusive composite interval mapping was carried out using SNP markers and Best Linear Unbiased Estimates of the phenotypic traits. A total of 23 QTLs were identified for eight agronomic traits and grain Fe and Zn concentration that explained 7.2 to 22.0% PV. A QTL by environment interaction analysis confirmed the stability of nine QTLs, including two QTLs for Zn on chromosomes 5 and 12. One epistatic interaction for plant height was significant with 28.4% PVE. Moreover, five QTLs were identified for Fe and Zn that harbor several candidate genes, e.g. OsZIP6 on QTL qZn5.1. A number of QTLs were associated with a combination of greater yield and increased grain Zn levels. These results are useful for development of new rice varieties with good agronomic traits and high grain Zn using MAS, and identification of genetic resources with the novel QTLs for grain Zn.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of genomic regions associated with agronomic and biofortification traits in DH populations of rice.PLoS One. 2018 Aug 10;13(8):e0201756. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0201756. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30096168 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of genomic region(s) responsible for high iron and zinc content in rice.Sci Rep. 2019 May 31;9(1):8136. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-43888-y. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31148549 Free PMC article.
-
Meta-analysis of grain iron and zinc associated QTLs identified hotspot chromosomal regions and positional candidate genes for breeding biofortified rice.Plant Sci. 2019 Nov;288:110214. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2019.110214. Epub 2019 Aug 8. Plant Sci. 2019. PMID: 31521222
-
Route and Regulation of Zinc, Cadmium, and Iron Transport in Rice Plants (Oryza sativa L.) during Vegetative Growth and Grain Filling: Metal Transporters, Metal Speciation, Grain Cd Reduction and Zn and Fe Biofortification.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Aug 13;16(8):19111-29. doi: 10.3390/ijms160819111. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26287170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
2Gs and plant architecture: breaking grain yield ceiling through breeding approaches for next wave of revolution in rice (Oryza sativa L.).Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2024 Feb;44(1):139-162. doi: 10.1080/07388551.2022.2112648. Epub 2022 Sep 29. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 36176065 Review.
Cited by
-
Omics-Facilitated Crop Improvement for Climate Resilience and Superior Nutritive Value.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Dec 1;12:774994. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.774994. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 34925418 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-Wide SNP Discovery and Mapping QTLs for Seed Iron and Zinc Concentrations in Chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.).Front Nutr. 2020 Oct 15;7:559120. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2020.559120. eCollection 2020. Front Nutr. 2020. PMID: 33154975 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the genetics underlying micronutrient signatures of diversity panel present in brown rice through genome-ionome linkages.Plant J. 2023 Feb;113(4):749-771. doi: 10.1111/tpj.16080. Epub 2023 Jan 18. Plant J. 2023. PMID: 36573652 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic prediction and QTL analysis for grain Zn content and yield in Aus-derived rice populations.J Plant Biochem Biotechnol. 2024;33(2):216-236. doi: 10.1007/s13562-024-00886-0. Epub 2024 May 9. J Plant Biochem Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 40308942 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic determinants of micronutrient traits in graminaceous crops to combat hidden hunger.Theor Appl Genet. 2021 Oct;134(10):3147-3165. doi: 10.1007/s00122-021-03878-z. Epub 2021 Jun 6. Theor Appl Genet. 2021. PMID: 34091694 Review.
References
-
- Ricepedia, Rice as a crop. [Online] Available from, http://ricepedia.org/rice-as-a-crop/rice-productivity (2019).
-
- Tripathy. SK, Dash M, Behera SK, Ithape DM, Maharana M. Nutrient rich quality rice- a journey to healthy life. Adv. Plants Agric. Res. 2017;7(5):364–367.
-
- Tripathi DK, et al. Micronutrients and their diverse role in agricultural crops: advances and future prospective. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2015;37:139. doi: 10.1007/s11738-015-1870-3. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

