Preclinical evaluation of a novel triple-acting PIM/PI3K/mTOR inhibitor, IBL-302, in breast cancer
- PMID: 32042115
- PMCID: PMC7118022
- DOI: 10.1038/s41388-020-1202-y
Preclinical evaluation of a novel triple-acting PIM/PI3K/mTOR inhibitor, IBL-302, in breast cancer
Abstract
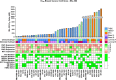
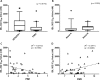
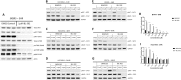
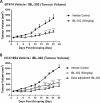
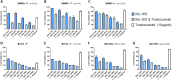
The proviral integration of Moloney virus (PIM) family of protein kinases are overexpressed in many haematological and solid tumours. PIM kinase expression is elevated in PI3K inhibitor-treated breast cancer samples, suggesting a major resistance pathway for PI3K inhibitors in breast cancer, potentially limiting their clinical utility. IBL-302 is a novel molecule that inhibits both PIM and PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling. We thus evaluated the preclinical activity of IBL-302, in a range of breast cancer models. Our results demonstrate in vitro efficacy of IBL-302 in a range of breast cancer cell lines, including lines with acquired resistance to trastuzumab and lapatinib. IBL-302 demonstrated single-agent, anti-tumour efficacy in suppression of pAKT, pmTOR and pBAD in the SKBR-3, BT-474 and HCC-1954 HER2+/PIK3CA-mutated cell lines. We have also shown the in vivo single-agent efficacy of IBL-302 in the subcutaneous BT-474 and HCC-1954 xenograft model in BALB/c nude mice. The combination of trastuzumab and IBL-302 significantly increased the anti-proliferative effect in HER2+ breast cancer cell line, and matched trastuzumab-resistant line, relative to testing either drug alone. We thus believe that the novel PIM and PI3K/mTOR inhibitor, IBL-302, represents an exciting new potential treatment option for breast cancer, and that it should be considered for clinical investigation.
Conflict of interest statement
MON and DC were shareholders and employees in Inflection Biosciences Ltd. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bachmann M, Möröy T, The serine/threonine kinase Pim-1. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2005;37:726–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

