Antibody-mediated delivery of viral epitopes to tumors harnesses CMV-specific T cells for cancer therapy
- PMID: 32042168
- PMCID: PMC7456461
- DOI: 10.1038/s41587-019-0404-8
Antibody-mediated delivery of viral epitopes to tumors harnesses CMV-specific T cells for cancer therapy
Abstract
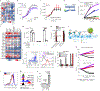
Several cancer immunotherapy approaches, such as immune checkpoint blockade and adoptive T-cell therapy, boost T-cell activity against the tumor, but these strategies are not effective in the absence of T cells specific for displayed tumor antigens. Here we outline an immunotherapy in which endogenous T cells specific for a noncancer antigen are retargeted to attack tumors. The approach relies on the use of antibody-peptide epitope conjugates (APECs) to deliver suitable antigens to the tumor surface for presention by HLA-I. To retarget cytomegalovirus (CMV)-specific CD8+ T cells against tumors, we used APECs containing CMV-derived epitopes conjugated to tumor-targeting antibodies via metalloprotease-sensitive linkers. These APECs redirect pre-existing CMV immunity against tumor cells in vitro and in mouse cancer models. In vitro, APECs activated specifically CMV-reactive effector T cells whereas a bispecific T-cell engager activated both effector and regulatory T cells. Our approach may provide an effective alternative in cancers that are not amenable to checkpoint inhibitors or other immunotherapies.
Figures

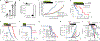
Comment in
-
Ubiquitous Virus-Targeted CD8+ T Cells Can Be Redirected to Tumors.Cancer Discov. 2020 Apr;10(4):OF1. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-RW2020-026. Epub 2020 Feb 21. Cancer Discov. 2020. PMID: 32086312
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

