CBP mediated DOT1L acetylation confers DOT1L stability and promotes cancer metastasis
- PMID: 32042335
- PMCID: PMC6993218
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.39013
CBP mediated DOT1L acetylation confers DOT1L stability and promotes cancer metastasis
Abstract
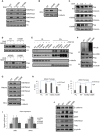
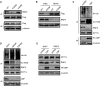
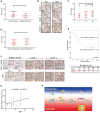
Background and Aim: DOT1L regulates various genes involved in cancer onset and progression by catalyzing H3K79 methylation, but how DOT1L activity itself is regulated is unclear. Here, we aimed to identify specific DOT1L post-translational modifications that might regulate DOT1L activity and thus impact on colorectal cancer (CRC) progression. Methods: We conducted affinity purification and mass spectrometry to explore DOT1L post-translational modifications. We then established transwell migration and invasion assays to specifically investigate the role of DOT1L(K358) acetylation on CRC cellular behavior in vitro and a bioluminescence imaging approach to determine the role of DOT1L(K358) acetylation in CRC metastasis in vivo. We performed chromatin immunoprecipitation to identify DOT1L acetylation-controlled target genes. Finally, we used immunohistochemical staining of human tissue arrays to examine the relevance of DOT1L(K358) acetylation in CRC progression and metastasis and the correlation between DOT1L acetylation and CBP. Results: We found that CBP mediates DOT1L K358 acetylation in human colon cancer cells and positively correlates with CRC stages. Mechanistically, DOT1L acetylation confers DOT1L stability by preventing the binding of RNF8 to DOT1L and subsequent proteasomal degradation, but does not affect its enzyme activity. Once stabilized, DOT1L can catalyze the H3K79 methylation of genes involved in epithelial-mesenchymal transition, including SNAIL and ZEB1. An acetylation mimic DOT1L mutant (Q358) could induce a cancer-like phenotype in vitro, characterized by metastasis and invasion. Finally, DOT1L(K358) acetylation correlated with CRC progression and a poor survival rate as well as with high CBP expression. Conclusions: DOT1L acetylation by CBP drives CRC progression and metastasis. Targeting DOT1L deacetylation signaling is a potential therapeutic strategy for DOT1L-driven cancers.
Keywords: Acetylation; CBP; DOT1L; Degradation; Metastasis.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Silencing or inhibition of H3K79 methyltransferase DOT1L induces cell cycle arrest by epigenetically modulating c-Myc expression in colorectal cancer.Clin Epigenetics. 2019 Dec 30;11(1):199. doi: 10.1186/s13148-019-0778-y. Clin Epigenetics. 2019. PMID: 31888761 Free PMC article.
-
Hesperetin promotes DOT1L degradation and reduces histone H3K79 methylation to inhibit gastric cancer metastasis.Phytomedicine. 2021 Apr;84:153499. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153499. Epub 2021 Feb 10. Phytomedicine. 2021. PMID: 33667841
-
Snail/FOXK1/Cyr61 Signaling Axis Regulates the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Metastasis in Colorectal Cancer.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;47(2):590-603. doi: 10.1159/000490015. Epub 2018 May 22. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29794466
-
The upstreams and downstreams of H3K79 methylation by DOT1L.Chromosoma. 2016 Sep;125(4):593-605. doi: 10.1007/s00412-015-0570-5. Epub 2016 Jan 4. Chromosoma. 2016. PMID: 26728620 Review.
-
Histone Methyltransferase DOT1L as a Promising Epigenetic Target for Treatment of Solid Tumors.Front Genet. 2022 Apr 13;13:864612. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.864612. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35495127 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Roles of Lysine Methylation in Glucose and Lipid Metabolism: Functions, Regulatory Mechanisms, and Therapeutic Implications.Biomolecules. 2024 Jul 19;14(7):862. doi: 10.3390/biom14070862. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39062577 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Post-Translational Modifications in Colorectal Cancer Metastasis.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Feb 3;16(3):652. doi: 10.3390/cancers16030652. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38339403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The DNA damage-independent ATM signalling maintains CBP/DOT1L axis in MLL rearranged acute myeloid leukaemia.Oncogene. 2024 Jun;43(25):1900-1916. doi: 10.1038/s41388-024-02998-2. Epub 2024 Apr 26. Oncogene. 2024. PMID: 38671157 Free PMC article.
-
The acetyltransferase BmCBP changes the acetylation modification of BmSP3 and affects its protein expression in silkworm, Bombyx mori.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Oct;50(10):8509-8521. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08699-5. Epub 2023 Aug 29. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37642757
-
PARP1-DOT1L transcription axis drives acquired resistance to PARP inhibitor in ovarian cancer.Mol Cancer. 2024 May 22;23(1):111. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02025-8. Mol Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38778348 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:87–108. - PubMed
-
- O'Connell JB, Maggard MA, Ko CY. Colon cancer survival rates with the new american joint committee on cancer sixth edition staging. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2004;96:1420–5. - PubMed
-
- Liefers GJ, Cleton-Jansen AM, van de Velde CJ, Hermans J, van Krieken JH, Cornelisse CJ. et al. Micrometastases and survival in stage ii colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:223–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

