Sulfur-containing amino acids in aged garlic extract inhibit inflammation in human gingival epithelial cells by suppressing intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression and IL-6 secretion
- PMID: 32042418
- PMCID: PMC7006171
- DOI: 10.3892/br.2019.1269
Sulfur-containing amino acids in aged garlic extract inhibit inflammation in human gingival epithelial cells by suppressing intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression and IL-6 secretion
Abstract
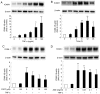
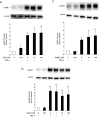
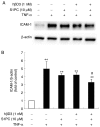
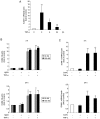
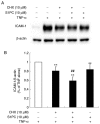
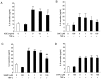
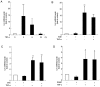
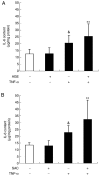
Aged garlic extract (AGE) contains various biologically active sulfur-containing amino acids, such as S-allylcysteine (SAC), S-1-propenylcysteine (S1PC) and S-allylmercaptocysteine (SAMC). These amino acids have been demonstrated to lower hypertension, improve atherosclerosis and enhance immunity through their anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities. It was recently reported that the administration of AGE alleviated gingivitis in a clinical trial. In this study, to gain insight into this effect of AGE, the authors examined whether AGE and the three above-mentioned sulfur compounds influence the effects of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) in inducing intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) expression and interleukin-6 (IL-6) secretion in Ca9-22 human gingival epithelial cells. It was found that S1PC reduced the level of ICAM-1 protein induced by TNF-α possibly through post-translational levels without affecting the TNF-α-induced mRNA expression. However, SAC and SAMC had no effect. It was also confirmed the inhibitory effect of an antimicrobial peptide [human-β defensin-3 (hβD3)] and found that the inhibitory effects of hbD3 and S1PC were synergistic. On the other hand, the TNF-α-induced IL-6 secretion was attenuated by SAC and SAMC in a dose-dependent manner, whereas S1PC was ineffective. In addition, SAC and SAMC, but not S1PC inhibited the phosphorylation of the transcription factor nuclear factor κ-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB), which is involved in the expression of inflammatory molecules, suggesting that the anti-inflammatory effects of SAC and SAMC are mediated, at least partly, by NF-κB. On the whole, the findings of this study suggest that the three sulfur amino acids in AGE function synergistically in alleviating inflammation in human gingival epithelial cells.
Keywords: ICAM-1; IL-6; aged garlic extract; gingival epithelial cells; inflammation; sulfur-containing amino acid.
Copyright © 2019, Spandidos Publications.
Figures
References
-
- Zini A, Mann J, Mazor S, Vered Y. The efficacy of aged garlic extract on gingivitis-A randomized clinical trial. J Clin Dentist. 2018;29:52–56. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
