MOF@PEDOT Composite Films for Impedimetric Pesticide Sensors
- PMID: 32042446
- PMCID: PMC7001120
- DOI: 10.1002/gch2.201900076
MOF@PEDOT Composite Films for Impedimetric Pesticide Sensors
Abstract
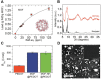
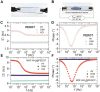
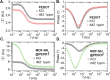
Due to its deleterious effects on health, development of new methods for detection and removal of pesticide residues in primary and derived agricultural products is a research topic of great importance. Among them, imazalil (IMZ) is a widely used post-harvest fungicide with good performances in general, and is particularly applied to prevent green mold in citrus fruits. In this work, a composite film for the impedimetric sensing of IMZ built from metal-organic framework nanocrystallites homogeneously distributed on a conductive poly(3,4-ethylene dioxythiophene) (PEDOT) layer is presented. The as-synthetized thin films are produced via spin-coating over poly(ethylene terephtalate (PET) substrate following a straightforward, cost-effective, single-step procedure. By means of impedance spectroscopy, electric transport properties of the films are studied, and high sensitivity towards IMZ concentration in the range of 15 ppb to 1 ppm is demonstrated (featuring 1.6 and 4.2 ppb limit of detection, when using signal modulus and phase, respectively). The sensing platform hereby presented could be used for the construction of portable, miniaturized, and ultrasensitive devices, suitable for pesticide detection in food, wastewater effluents, or the assessment of drinking-water quality.
Keywords: PEDOT; conductive polymers; imazalil; impedance spectroscopy; metal–organic frameworks; pesticide sensors.
© 2020 The Authors. Published by WILEY‐VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Natural Biostimulants Elicit Plant Immune System in an Integrated Management Strategy of the Postharvest Green Mold of Orange Fruits Incited by Penicillium digitatum.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Jun 15;12:684722. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.684722. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 34211489 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrafast and Large-Scale Fabrication of PEDOT:PSS Nanofilms Using Electrical-Field-Assisted Direct Ink Deposition.Molecules. 2023 Aug 10;28(16):5989. doi: 10.3390/molecules28165989. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37630240 Free PMC article.
-
Highly sensitive ethylene glycol-doped PEDOT-PSS organic thin films for LPG sensing.RSC Adv. 2018 May 16;8(32):18074-18083. doi: 10.1039/c8ra01061g. eCollection 2018 May 14. RSC Adv. 2018. PMID: 35542062 Free PMC article.
-
Modifying the conductive properties of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) thin films in green solvents.Front Chem. 2022 Sep 12;10:1005266. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2022.1005266. eCollection 2022. Front Chem. 2022. PMID: 36171993 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PEDOT:PSS-Based Conductive Textiles and Their Applications.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Mar 28;20(7):1881. doi: 10.3390/s20071881. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32231114 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ionic self-assembly of redox-active polyelectrolyte-surfactant complexes: mesostructured soft materials for electrochemical nanoarchitectonics.Sci Technol Adv Mater. 2025 Apr 29;26(1):2497309. doi: 10.1080/14686996.2025.2497309. eCollection 2025. Sci Technol Adv Mater. 2025. PMID: 40458735 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preparation of Smart Surfaces Based on PNaSS@PEDOT Microspheres: Testing of E. coli Detection.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Apr 5;22(7):2784. doi: 10.3390/s22072784. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35408397 Free PMC article.
-
Metal-Organic-Framework-Derived Nanostructures as Multifaceted Electrodes in Metal-Sulfur Batteries.Adv Mater. 2021 Jul;33(27):e2008784. doi: 10.1002/adma.202008784. Epub 2021 May 25. Adv Mater. 2021. PMID: 34031929 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Spanoghe B. M. P., Pesticides – Formulations, Effects, Fate, InTech, London, UK: 2011.
-
- Pimentel D., Burgess M., in Integrated Pest Management (Eds: Pimentel D., Peshin R.), Springer, Netherlands: 2014, pp. 47–71.
-
- Van Cutsem J., Van Gerven F., Janssen P. A., Mycoses 1988, 31, 143. - PubMed
-
- Altieri G., Di Renzo G. C., Genovese F., Calandra M., Strano M. C., Biosyst. Eng. 2013, 115, 434.
-
- Su H. C., Lin A. Y., J. Food Drug Anal. 2003, 11, 296.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

