High Blood Pressure-A High Risk Problem for Public Healthcare
- PMID: 32042451
- PMCID: PMC6993761
- DOI: 10.12865/CHSJ.45.03.01
High Blood Pressure-A High Risk Problem for Public Healthcare
Abstract
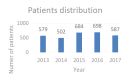
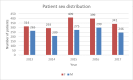
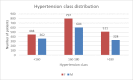
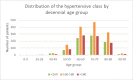
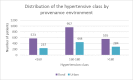
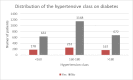
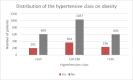
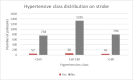
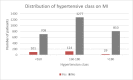
High blood pressure is the most common cardiovascular disease and the first one due to mortality risk. Prospective studies showed that, until 2025, the number of individuals with HBP will increase up to 1.56 billion in adults, of which more than two thirds will be found in poor countries or developing ones. In the present study, we evaluated the clinical and epidemiological aspects of HBP in a group of 3050 patients admitted in the Department of Cardiology of the Public Hospital of Caracal, Olt county. The study on the distribution of patients according to sex allowed us to observe that most patients suffering from HBP were women, while the distribution according to the social environment showed that more than 2/3 of high blood pressure patients came from the rural area. By studying the distribution of patients according to age, we observed that most HBP patients were aged over 60 years old (86.49%).
Keywords: High blood pressure; cardiovascular diseases; mortality.
Copyright © 2019, Medical University Publishing House Craiova.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Orthostatic low blood pressure in patient suffering from hypertension, in external cardiology consultation].Mali Med. 2015;30(4):21-25. Mali Med. 2015. PMID: 29927130 French.
-
Changes in blood pressure among users of lay health worker or volunteer operated community-based blood pressure programs over time: a systematic review protocol.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015 Oct;13(10):30-40. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2015-1927. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015. PMID: 26571280
-
[Severe high blood pressure recently diagnosed in an urban milieu from Subsahelian Africa: Epidemiologic, clinical, therapeutic and evolutionary aspects].Ann Cardiol Angeiol (Paris). 2019 Oct;68(4):241-248. doi: 10.1016/j.ancard.2019.07.014. Epub 2019 Aug 27. Ann Cardiol Angeiol (Paris). 2019. PMID: 31471040 French.
-
Blood pressure, systolic and diastolic, and cardiovascular risks. US population data.Arch Intern Med. 1993 Mar 8;153(5):598-615. doi: 10.1001/archinte.153.5.598. Arch Intern Med. 1993. PMID: 8439223 Review.
-
Prevention of suicide and attempted suicide in Denmark. Epidemiological studies of suicide and intervention studies in selected risk groups.Dan Med Bull. 2007 Nov;54(4):306-69. Dan Med Bull. 2007. PMID: 18208680 Review.
Cited by
-
Exercise-Induced Excessive Blood Pressure Elevation Is Associated with Cardiac Dysfunction in Male Patients with Essential Hypertension.Int J Hypertens. 2022 Nov 28;2022:8910453. doi: 10.1155/2022/8910453. eCollection 2022. Int J Hypertens. 2022. PMID: 36479241 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lim SS, Vos T, Flaxman AD, Danaei G, Shibuya K, Adair-Rohani H, et al. A comparative risk assessment of burden of disease and injury attributable to 67 risk factors and risk factor clusters in 21 regions, 1990-2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380:2224–2260. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lopez AD, Mathers CD, Ezzati M, Jamison DT, Murray CJ. Global and regional burden of disease and risk factors, 2001: systematic analysis of population health data. Lancet. 2006;367:1747–1757. - PubMed
-
- Mokdad AH, Forouzanfar MH, Daoud F, Mokdad AA, El Bcheraoui C, Moradi-Lakeh M, et al. Global burden of diseases, injuries, and risk factors for young people’s health during 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2016;387:2383–2401. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
