Sensitive, quantitative detection of Besnoitia darlingi and related parasites in intermediate hosts and to assess felids as definitive hosts for known and as-yet undescribed related parasite species
- PMID: 32042587
- PMCID: PMC7000450
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijppaw.2020.01.011
Sensitive, quantitative detection of Besnoitia darlingi and related parasites in intermediate hosts and to assess felids as definitive hosts for known and as-yet undescribed related parasite species
Abstract
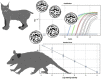
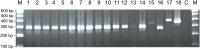
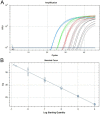
Besnoitia darlingi, B. neotomofelis and B. oryctofelisi are closely related coccidian parasites with cats as definitive hosts. While B. darlingi uses opossums as intermediate hosts, B. neotomofelis and B. oryctofelisi have been described in Southern Plains woodrats (Neotoma micropus) from the USA and in domestic rabbits from Argentina, respectively. A comparison of the Internal Transcribed Spacer-1 (ITS-1) region of the ribosomal DNA (rDNA) of these Besnoitia spp. showed only a few differences. The present study aimed at developing a real-time PCR to detect B. darlingi, B. neotomofelis and B. oryctofelisi in tissues of intermediate and in faeces of definitive hosts in order to support studies of these organisms' epidemiology and pathogenesis. The established PCR was based on primer regions distinct from the ITS-1 sequences of ungulate Besnoitia spp. and made use of a Besnoitia universal probe. To monitor inhibition, a heterologous internal control was established based on the enhanced green fluorescent protein gene. The real-time PCR reacted with B. darlingi, B. neotomofelis and B. oryctofelisi, while the novel PCR did not recognize ungulate Besnoitia spp. (B. besnoiti, B. bennetti, B. tarandi). DNA of Apicomplexa ascribed to other Besnoitia-related genera, including other gut parasites of cats (Cryptosporidium parvum, Giardia duodenalis, Tritrichomonas foetus), was not recognized. The real-time PCR had an analytic sensitivity of less than 1 tachyzoite per reaction. In feline faeces spiked with B. darlingi oocysts, the limit of detection was a DNA amount equivalent to 1 oocyst per PCR reaction. In B. darlingi infected ɣ-interferon knock-out mice, the lung was identified as the predilection organ. In conclusion, this real-time PCR should advance further studies on these parasites and may inspire research on related species, not only in the Americas, but also in other parts of the world.
Keywords: Besnoitia darlingi; Besnoitia neotomofelis; Besnoitia oryctofelisi; Besnoitiosis; Lagomorph; Primer; Real-time PCR; Rodent.
© 2020 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The study described is original and is not under consideration by any other journal. All authors approved the final manuscript and its submission. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Molecular analysis suggests that Namibian cheetahs (Acinonyx jubatus) are definitive hosts of a so far undescribed Besnoitia species.Parasit Vectors. 2021 Apr 14;14(1):201. doi: 10.1186/s13071-021-04697-3. Parasit Vectors. 2021. PMID: 33853647 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative real time polymerase chain reaction assays for the sensitive detection of Besnoitia besnoiti infection in cattle.Vet Parasitol. 2011 Jun 10;178(3-4):208-16. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2011.01.038. Epub 2011 Feb 15. Vet Parasitol. 2011. PMID: 21324596
-
Serological response of cats to experimental Besnoitia darlingi and Besnoitia neotomofelis infections and prevalence of antibodies to these parasites in cats from Virginia and Pennsylvania.J Parasitol. 2011 Apr;97(2):259-61. doi: 10.1645/GE-2626.1. Epub 2010 Oct 27. J Parasitol. 2011. PMID: 21506782
-
An update on epidemiology and clinical aspects of besnoitiosis in livestock and wildlife in sub-Saharan Africa: A systematic review.Parasite Epidemiol Control. 2023 Jan 13;21:e00284. doi: 10.1016/j.parepi.2023.e00284. eCollection 2023 May. Parasite Epidemiol Control. 2023. PMID: 36793766 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[New methods for the diagnosis of Cryptosporidium and Giardia].Parassitologia. 2004 Jun;46(1-2):151-5. Parassitologia. 2004. PMID: 15305706 Review. Italian.
Cited by
-
Drivers of infection with Toxoplasma gondii genotype type II in Eurasian red squirrels (Sciurus vulgaris).Parasit Vectors. 2024 Jan 23;17(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s13071-023-06068-6. Parasit Vectors. 2024. PMID: 38263195 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular analysis suggests that Namibian cheetahs (Acinonyx jubatus) are definitive hosts of a so far undescribed Besnoitia species.Parasit Vectors. 2021 Apr 14;14(1):201. doi: 10.1186/s13071-021-04697-3. Parasit Vectors. 2021. PMID: 33853647 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced neural progenitor cell count and cortical neurogenesis in guinea pigs congenitally infected with Toxoplasma gondii.Commun Biol. 2023 Nov 27;6(1):1209. doi: 10.1038/s42003-023-05576-6. Commun Biol. 2023. PMID: 38012384 Free PMC article.
-
A putative new Besnoitia species in the southern black-eared opossum Didelphis aurita.Int J Parasitol Parasites Wildl. 2024 Sep 21;25:100998. doi: 10.1016/j.ijppaw.2024.100998. eCollection 2024 Dec. Int J Parasitol Parasites Wildl. 2024. PMID: 39376793 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment and validation of a guinea pig model for human congenital toxoplasmosis.Parasit Vectors. 2021 Aug 6;14(1):389. doi: 10.1186/s13071-021-04890-4. Parasit Vectors. 2021. PMID: 34362413 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dubey J.P., Lindsay D.S., Rosenthal B.M., Sreekumar C., Hill D.E., Shen S.K., Kwok O.C., Rickard L.G., Black S.S., Rashmir-Raven A. Establishment of Besnoitia darlingi from opossums (Didelphis virginiana) in experimental intermediate and definitive hosts, propagation in cell culture, and description of ultrastructural and genetic characteristics. Int. J. Parasitol. 2002;32:1053–1064. - PubMed
-
- Dubey J.P., Sreekumar C., Lindsay D.S., Hill D., Rosenthal B.M., Venturini L., Venturini M.C., Greiner E.C. Besnoitia oryctofelisi n. sp. (Protozoa: Apicomplexa) from domestic rabbits. Parasitology. 2003;126:521–539. - PubMed
-
- Dubey J.P., Sreekumar C., Rosenthal B.M., Lindsay D.S., Grisard E.C., Vitor R.W. Biological and molecular characterization of Besnoitia akodoni n.sp. (Protozoa: Apicomplexa) from the rodent Akodon montensis in Brazil. Parassitologia. 2003;45:61–70. - PubMed
-
- Dubey J.P., Yabsley M.J. Besnoitia neotomofelis n. sp. (Protozoa: Apicomplexa) from the southern plains woodrat ( Neotoma micropus) Parasitology. 2010;137:1731–1747. - PubMed
-
- Ernst J.V., Chobotar B., Oaksec, Hammond D.M. Besnoitia jellisoni (Sporozoa: Toxoplasmea) in rodents from Utah and California. J. Parasitol. 1968;54:545–549. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

