Diagnostic value of an automated breast volume scanner compared with a hand-held ultrasound: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 32042678
- PMCID: PMC6989916
- DOI: 10.21037/gs.2019.11.18
Diagnostic value of an automated breast volume scanner compared with a hand-held ultrasound: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: The diagnostic performance of an automated breast volume scanner (ABVS) compared with that of a hand-held ultrasound (HHUS) for breast cancer remains unclear. We performed a meta-analysis to compare the diagnostic performances of the ABVS and HHUS for breast cancer.
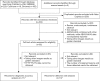
Methods: We searched PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane, and SinoMed databases to identify eligible studies up until November 14, 2018. Studies comparing ABVS and HHUS for differentiating benign and malignant breast tumors were included. A meta-analysis was performed to generate pooled diagnostic accuracy parameters [sensitivity, specificity, diagnostic odds ratio (DOR), area under the curve (AUC), and the Q* index] and detection rates for ABVS and HHUS.
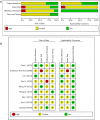
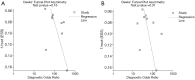
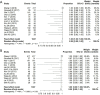
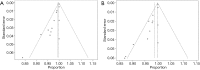
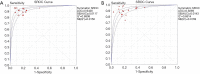
Results: Nine studies involving 1,376 patients and 1,527 lesions were included in the meta-analysis for diagnostic accuracy. The pooled sensitivity was 0.93 [95% confidence interval (CI), 0.91-0.95] for ABVS and 0.90 (95% CI, 0.88-0.92) for HHUS, and the pooled specificity was 0.86 (95% CI, 0.83-0.88) for ABVS and 0.82 (95% CI, 0.79-0.84) for HHUS. The pooled DOR was 88.66 (95% CI, 51.44-152.78) for ABVS and 41.06 for HHUS (95% CI, 26.58-63.42). The AUC of the summary receiver operating characteristic (SROC) was 0.9496 for ABVS and 0.9143 for HHUS, and the Q* index was 0.8899 for ABVS and 0.8469 for HHUS. Meta-regression showed no significant difference between the diagnostic accuracy of ABVS and HHUS (P=0.0771). No publication bias was found. Thirteen published studies involving 1,047 pathologically confirmed malignant lesions were included to generate a pooled detection rate. The pooled detection rate was 1.00 (95% CI, 1.00-1.00) for both ABVS and HHUS, for which a publication bias was found.
Conclusions: ABVS can be used as an appropriate screening tool for breast cancer as well as HHUS in diagnostic accuracy and detection rate. Considering other advantages of ABVS including non-radioactivity, sensitivity to dense breast, three-dimensional reconstruction, time-saving and repeatability, it might be a promising screening tool for young or dense-breast women in the future.
Keywords: Automated breast volume scanner (ABVS); breast cancer; hand-held ultrasound (HHUS); meta-analysis.
2019 Gland Surgery. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Diagnostic performance of combined use of automated breast volume scanning & hand-held ultrasound for breast lesions.Indian J Med Res. 2021 Aug;154(2):347-354. doi: 10.4103/ijmr.IJMR_836_19. Indian J Med Res. 2021. PMID: 35295015 Free PMC article.
-
Automated Breast Volume Scanner Is More Valuable Than Hand-Held Ultrasound in Diagnosis of Small Breast cancer: An Analysis of 725 Patients With 912 Lesions Evaluations.Ultrasound Q. 2024 Mar 1;40(1):66-73. doi: 10.1097/RUQ.0000000000000673. Ultrasound Q. 2024. PMID: 38436374
-
Diagnostic accuracy of automated breast volume scanning, hand-held ultrasound and molybdenum-target mammography for breast lesions: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Gland Surg. 2025 Mar 31;14(3):294-304. doi: 10.21037/gs-24-135. Epub 2025 Mar 26. Gland Surg. 2025. PMID: 40256474 Free PMC article.
-
Automatic Breast Volume Scanner versus Handheld Ultrasound in Differentiation of Benign and Malignant Breast Lesions: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2019 Aug;45(8):1874-1881. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2019.04.028. Epub 2019 May 24. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 31130410
-
Evaluation of Diagnostic Performance of Automatic Breast Volume Scanner Compared to Handheld Ultrasound on Different Breast Lesions: A Systematic Review.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Feb 19;12(2):541. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12020541. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35204629 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A multi-centre, randomised trial for diagnostic efficacy of the automatic breast volume scanner ultrasound for breast cancer screening in China.Front Oncol. 2025 Jan 21;14:1421425. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1421425. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39906662 Free PMC article.
-
Automated breast US as the primary screening test for breast cancer among East Asian women aged 40-49 years: a multicenter prospective study.Eur Radiol. 2021 Oct;31(10):7771-7782. doi: 10.1007/s00330-021-07864-3. Epub 2021 Mar 29. Eur Radiol. 2021. PMID: 33779816
-
Apparent diffusion coefficient magnetic resonance imaging (ADC-MRI) in the axillary breast cancer lymph node metastasis detection: a narrative review.Gland Surg. 2020 Dec;9(6):2225-2234. doi: 10.21037/gs-20-546. Gland Surg. 2020. PMID: 33447575 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Innovative integration of automated breast volume scan and ultrasound elastography for enhanced differentiation of benign and malignant breast lesions.Sci Rep. 2025 May 29;15(1):18816. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-01061-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40442122 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic reprogramming enables the auxiliary diagnosis of breast cancer by automated breast volume scanner.Front Oncol. 2022 Oct 12;12:939606. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.939606. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36313729 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
