Clonal dissemination of KPC-2-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae ST11 and ST48 clone among multiple departments in a tertiary teaching hospital in Jiangsu Province, China
- PMID: 32042732
- PMCID: PMC6990001
- DOI: 10.21037/atm.2019.12.01
Clonal dissemination of KPC-2-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae ST11 and ST48 clone among multiple departments in a tertiary teaching hospital in Jiangsu Province, China
Abstract
Background: The world-wide prevalence of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae (CRKP) poses a threat to the public health. The objective of this study was to determine the epidemiological and molecular patterns of KPC-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae (K. pneumoniae) clinical isolates.
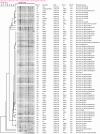
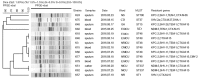
Methods: In this study, a total of 82 non-duplicated CRKP isolates were analyzed for the prevalence of resistant determinants including carbapenemase, extended spectrum β-lactamase (ESBLs), and AmpC as well as integrons and cassette regions by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and DNA sequencing. The genetic relatedness was investigated by pulsed field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) and multi-locus sequencing typing (MLST).
Results: Overall, bla KPC-2 (n=75) was the predominant carbapenemase gene, followed by high prevalence of bla SHV (92.7%) and bla CTX-M (90.2%). PFGE and MLST analysis revealed that 65 out of 68 KPC-2-producing CRKP belonged to the ST11 clone and were distributed mainly in the department of neurology ICU. Moreover, first report on clonal dissemination of KPC-2-producing CRKP ST48 clone and NDM-5-producing CRKP ST337 clone was also identified. Class I integron were detected in 17 (20.7%) of 82 isolates with aadA2 being the most common cassette. And a novel cassette array of integron, aac(6')-II-bla CARB/PSE-1 was identified.
Conclusions: All in all, KPC-2-producing CRKP ST11 and ST48 clone were widely disseminated in multiple departments of our hospital, which triggers the need for active surveillance and implementation of infection control measures.
Keywords: Carbapenemases; KPC-2; Klebsiella pneumoniae (K. pneumoniae); NDM-5; clonal dissemination.
2019 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical Molecular Epidemiology of Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Among Pediatric Patients in Jiangsu Province, China.Infect Drug Resist. 2020 Dec 22;13:4627-4635. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S293206. eCollection 2020. Infect Drug Resist. 2020. PMID: 33376368 Free PMC article.
-
Outbreak by Ventilator-Associated ST11 K. pneumoniae with Co-production of CTX-M-24 and KPC-2 in a SICU of a Tertiary Teaching Hospital in Central China.Front Microbiol. 2016 Aug 2;7:1190. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01190. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27531996 Free PMC article.
-
Emergence and nosocomial spread of ST11 carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae co-producing OXA-48 and KPC-2 in a regional hospital in Taiwan.J Med Microbiol. 2018 Jul;67(7):957-964. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.000771. J Med Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29873627
-
Multidrug Resistance Mechanisms of Carbapenem Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Strains Isolated in Chongqing, China.Ann Lab Med. 2017 Sep;37(5):398-407. doi: 10.3343/alm.2017.37.5.398. Ann Lab Med. 2017. PMID: 28643488 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance Phenotype and Molecular Epidemiology of Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolated from Nanjing Children's Hospital in Jiangsu Province, China.Infect Drug Resist. 2022 Sep 14;15:5435-5447. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S377068. eCollection 2022. Infect Drug Resist. 2022. PMID: 36131812 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Genomic Analysis of KPC-2-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae ST11 Isolates at the Respiratory Department of a Tertiary Care Hospital in Beijing, China.Front Microbiol. 2022 Jun 16;13:929826. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.929826. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35783384 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a phage-derived depolymerase specific for KL64 capsule of Klebsiella pneumoniae and its anti-biofilm effect.Virus Genes. 2021 Oct;57(5):434-442. doi: 10.1007/s11262-021-01847-8. Epub 2021 Jun 22. Virus Genes. 2021. PMID: 34156584
-
Molecular Epidemiology and Drug Resistant Mechanism of Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in Elderly Patients With Lower Respiratory Tract Infection.Front Public Health. 2021 May 20;9:669173. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.669173. eCollection 2021. Front Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34095072 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic insights and antimicrobial resistance profiles of CRKP and non-CRKP isolates in a Beijing geriatric medical center: emphasizing the blaKPC-2 carrying high-risk clones and their spread.Front Microbiol. 2024 Feb 13;15:1359340. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1359340. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38414769 Free PMC article.
-
Drug Susceptibility and Molecular Epidemiology of Klebsiella pneumoniae Bloodstream Infection in ICU Patients in Shanghai, China.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Oct 13;8:754944. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.754944. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34722591 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
