Epigenetic hypomethylation and upregulation of GD3s in triple negative breast cancer
- PMID: 32042739
- PMCID: PMC6990030
- DOI: 10.21037/atm.2019.12.23
Epigenetic hypomethylation and upregulation of GD3s in triple negative breast cancer
Erratum in
-
Erratum to epigenetic hypomethylation and upregulation of GD3s in triple negative breast cancer.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Sep;10(18):1042. doi: 10.21037/atm-2022-48. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36267729 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Breast cancer remains a major health problem in the world. Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is an aggressive subtype with very poor prognosis. Up to now, the mechanism behind TNBC's activity is still unclear and no candidate drug target has been identified. Thus, it is of critical importance to elucidate the pathways in TNBC and identify the relevant biomarkers. Recent studies showed that ganglioside D3 synthase (GD3s) played a very important role in development of cancers. However, the physiological functions and associated pathways of GD3s in TNBC are still unclear.
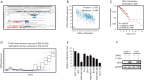
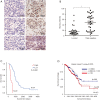
Methods: In silico analysis of the expression of GD3s in TNBC was conducted using The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and Oncomine databases. The proliferation of breast cancer cells was measured by MTT assay, colony formation by the soft agar method, and migration and invasion using Boyden chamber inserts. The methylation level of the gene encoding GD3s, ST8SIA1, in specimens was assessed by qMS-PCR and in silico using the UCSC gene browser. Protein expression was examined via immunohistochemistry (IHC), qRT-PCR and Western immunoblotting.
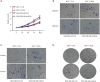
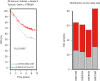
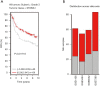
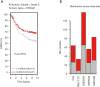
Results: In silico analysis showed a higher GD3s expression in ER- than ER+ breast cancers and GD3s was also highly expressed in TNBC compared to other types of breast cancers. The elevated GD3s expression in TNBC cells and tissues was associated with hypomethylation of the ST8SIA1 gene. Overexpression of GD3s in human breast cancer cells increased their proliferation, migration, invasion and colony formation ability. GD3s expression in breast cancers was closely associated with relapse-free survival (RFS) and overall survival (OS).
Conclusions: In summary, these results suggest that GD3s may be a potential biomarker and drug target in treatment of TNBC.
Keywords: Ganglioside D3 synthase (GD3s); biomarker; methylation; prognosis; triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC).
2019 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Disialyl GD2 ganglioside suppresses ICAM-1-mediated invasiveness in human breast cancer MDA-MB231 cells.Int J Biol Sci. 2017 Feb 12;13(3):265-275. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.16903. eCollection 2017. Int J Biol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28367091 Free PMC article.
-
Hypomethylation of ATP1A1 Is Associated with Poor Prognosis and Cancer Progression in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Apr 25;16(9):1666. doi: 10.3390/cancers16091666. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38730618 Free PMC article.
-
GD3 synthase regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis in breast cancer.Oncogene. 2015 Jun 4;34(23):2958-67. doi: 10.1038/onc.2014.245. Epub 2014 Aug 11. Oncogene. 2015. PMID: 25109336 Free PMC article.
-
SPAG5 upregulation contributes to enhanced c-MYC transcriptional activity via interaction with c-MYC binding protein in triple-negative breast cancer.J Hematol Oncol. 2019 Feb 8;12(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s13045-019-0700-2. J Hematol Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30736840 Free PMC article.
-
Ganglioside GD3 synthase (GD3S), a novel cancer drug target.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2018 Sep;8(5):713-720. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2018.07.009. Epub 2018 Jul 25. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2018. PMID: 30245960 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Distinct Roles of Sialyltransferases in Cancer Biology and Onco-Immunology.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 17;12:799861. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.799861. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34975914 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic Regulation of Glycosylation in Cancer and Other Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 15;22(6):2980. doi: 10.3390/ijms22062980. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33804149 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Ying and Yang of Ganglioside Function in Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Nov 10;15(22):5362. doi: 10.3390/cancers15225362. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38001622 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ST8SIA1 inhibition sensitizes triple negative breast cancer to chemotherapy via suppressing Wnt/β-catenin and FAK/Akt/mTOR.Clin Transl Oncol. 2021 Apr;23(4):902-910. doi: 10.1007/s12094-020-02484-7. Epub 2020 Sep 16. Clin Transl Oncol. 2021. PMID: 32939659
-
Role of Sialyl-O-Acetyltransferase CASD1 on GD2 Ganglioside O-Acetylation in Breast Cancer Cells.Cells. 2021 Jun 11;10(6):1468. doi: 10.3390/cells10061468. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34208013 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
