Restoration of FKBP51 protein promotes the progression of castration resistant prostate cancer
- PMID: 32042745
- PMCID: PMC6990039
- DOI: 10.21037/atm.2019.11.127
Restoration of FKBP51 protein promotes the progression of castration resistant prostate cancer
Abstract
Background: As deregulation of androgen receptor (AR) signaling target genes is associated with tumorigenesis and the development of prostate cancer (PCa), AR signaling is the primary therapeutic target for PCa. Although patients initially responses to first-line androgen deprivation therapies (ADTs), most of them with advanced PCa progress to lethal castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). Recent studies have suggested the molecular mechanisms by which AR elicit the robust up-regulation of the FKBP51 gene. We suggest that restored expression of FKBP51 gene, modulated by androgen receptor splicing variant 7 (AR-V7) which replaces full length androgen receptor (AR-FL) in androgen ablation status, promotes CRPC progression through activating NF-κB signaling.
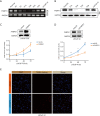
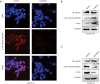
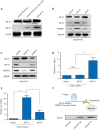
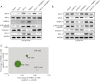
Methods: Immunohistochemistry assays were used to detect the expression of AR-V7, FKBP51 and NF-κB signaling correlated proteins in CRPC tissues. An androgen ablation resistant PCa cell line model established by Long-term culturing in androgen depleted medium, named androgen-independent LNCaP (LNCaP-AI) cells, were used to dynamically monitor FKBP51 expression during the process of androgen dependent PCa cells transforming into androgen-independent cells, as well as its association with NF-κB signal pathway. LNCaP-AI cell line was determined to express AR-V7 protein continuously. Luciferase reporter assays and DNA pull down were used to determine the association between AR-V7 and FKBP51.
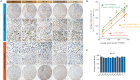
Results: Our results suggested that CRPC patients with AR-V7 high expression tend to have higher expression of FKBP51 and enhanced NF-κB signaling compared with AR-V7 negative patients. Knockdown of AR-V7 or FKBP51 in LNCaP-AI cells attenuated the level of p-NF-κB (Ser536) and androgen-resistant cells growth. Luciferase reporter assays and DNA pull down results indicated that FKBP51 was transcriptionally promoted by AR-V7 in absence of androgen, which enhanced NF-κB signaling.
Conclusions: Because of upregulation of AR-V7 in androgen-independent PCa cells, increasing of FKBP51 induced NF-κB signaling, leading to progression of CRPC.
Keywords: AR-V7; Castration resistant prostate cancer; FKBP51; NF-κB.
2019 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Melatonin Inhibits Androgen Receptor Splice Variant-7 (AR-V7)-Induced Nuclear Factor-Kappa B (NF-κB) Activation and NF-κB Activator-Induced AR-V7 Expression in Prostate Cancer Cells: Potential Implications for the Use of Melatonin in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer (CRPC) Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 May 31;18(6):1130. doi: 10.3390/ijms18061130. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28561752 Free PMC article.
-
Transcript Levels of Androgen Receptor Variant 7 and Ubiquitin-Conjugating Enzyme 2C in Hormone Sensitive Prostate Cancer and Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer.Prostate. 2017 Jan;77(1):60-71. doi: 10.1002/pros.23248. Epub 2016 Aug 22. Prostate. 2017. PMID: 27550197
-
Ratio of the expression levels of androgen receptor splice variant 7 to androgen receptor in castration refractory prostate cancer.Oncol Lett. 2021 Dec;22(6):831. doi: 10.3892/ol.2021.13092. Epub 2021 Oct 13. Oncol Lett. 2021. PMID: 34691258 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Origin, Expression Regulation, and Biological Function of Androgen Receptor Splicing Variant 7 in Prostate Cancer.Urol Int. 2021;105(5-6):337-353. doi: 10.1159/000510124. Epub 2020 Sep 21. Urol Int. 2021. PMID: 32957106 Review.
-
Prognostic Value of Androgen Receptor Splice Variant 7 in the Treatment of Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer with Next generation Androgen Receptor Signal Inhibition: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Eur Urol Focus. 2018 Jul;4(4):529-539. doi: 10.1016/j.euf.2017.01.004. Epub 2017 Jan 23. Eur Urol Focus. 2018. PMID: 28753843
Cited by
-
Structure and function of the TPR-domain immunophilins FKBP51 and FKBP52 in normal physiology and disease.J Cell Biochem. 2024 Dec;125(12):e30406. doi: 10.1002/jcb.30406. Epub 2023 Apr 23. J Cell Biochem. 2024. PMID: 37087733 Review.
-
CRPC Membrane-Camouflaged, Biomimetic Nanosystem for Overcoming Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer by Cellular Vehicle-Aided Tumor Targeting.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 26;23(7):3623. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073623. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35408983 Free PMC article.
-
Rapamycin inhibits AR signaling pathway in prostate cancer by interacting with the FK1 domain of FKBP51.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2020 Jul 16;23:100778. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2020.100778. eCollection 2020 Sep. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2020. PMID: 32695889 Free PMC article.
-
Androgen Receptor Upregulates Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue 1 to Induce NF-κB Activity via Androgen-Dependent and -Independent Pathways in Prostate Carcinoma Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 26;24(7):6245. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076245. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37047218 Free PMC article.
-
FKBP51 promotes invasion and migration by increasing the autophagic degradation of TIMP3 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Oct 1;12(10):899. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-04192-8. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 34599146 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
