Fine intercellular connections in development: TNTs, cytonemes, or intercellular bridges?
- PMID: 32043076
- PMCID: PMC6997949
- DOI: 10.15698/cst2020.02.212
Fine intercellular connections in development: TNTs, cytonemes, or intercellular bridges?
Abstract
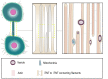
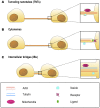
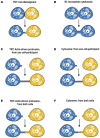
Intercellular communication is a fundamental property of multicellular organisms, necessary for their adequate responses to changing environment. Tunneling nanotubes (TNTs) represent a novel means of intercellular communication being a long cell-to-cell conduit. TNTs are actively formed under a broad range of stresses and are also proposed to exist under physiological conditions. Development is a physiological condition of particular interest, as it requires fine coordination. Here we discuss whether protrusions shown to exist during embryonic development of different species could be TNTs or if they represent other types of cell structure, like cytonemes or intercellular bridges, that are suggested to play an important role in development.
Keywords: TNTs; cytonemes; intercellular bridges; intercellular communication; tunneling nanotubes.
Copyright: © 2020 Korenkova et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tunneling nanotubes enable intercellular transfer in zebrafish embryos.Dev Cell. 2025 Feb 24;60(4):524-534.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2024.10.016. Epub 2024 Nov 13. Dev Cell. 2025. PMID: 39541978
-
Identification and Characterization of Tunneling Nanotubes for Intercellular Trafficking.Curr Protoc. 2023 Nov;3(11):e939. doi: 10.1002/cpz1.939. Curr Protoc. 2023. PMID: 37994667
-
Multifaceted roles of tunneling nanotubes in intercellular communication.Front Physiol. 2012 Apr 10;3:72. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2012.00072. eCollection 2012. Front Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22514537 Free PMC article.
-
Tunneling Nanotubes and Tumor Microtubes in Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Apr 1;12(4):857. doi: 10.3390/cancers12040857. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32244839 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell communication by tunneling nanotubes: Implications in disease and therapeutic applications.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Feb;234(2):1130-1146. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27072. Epub 2018 Sep 12. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30206931 Review.
Cited by
-
Programmed disassembly of a microtubule-based membrane protrusion network coordinates 3D epithelial morphogenesis in Drosophila.EMBO J. 2024 Feb;43(4):568-594. doi: 10.1038/s44318-023-00025-w. Epub 2024 Jan 23. EMBO J. 2024. PMID: 38263333 Free PMC article.
-
Tunneling Nanotube: An Enticing Cell-Cell Communication in the Nervous System.Biology (Basel). 2023 Sep 27;12(10):1288. doi: 10.3390/biology12101288. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37886998 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multicellularity and the Need for Communication-A Systematic Overview on (Algal) Plasmodesmata and Other Types of Symplasmic Cell Connections.Plants (Basel). 2023 Sep 21;12(18):3342. doi: 10.3390/plants12183342. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37765506 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hijacking intercellular trafficking for the spread of protein aggregates in neurodegenerative diseases: a focus on tunneling nanotubes (TNTs).Extracell Vesicles Circ Nucl Acids. 2023 Mar 9;4(1):27-43. doi: 10.20517/evcna.2023.05. eCollection 2023. Extracell Vesicles Circ Nucl Acids. 2023. PMID: 39698299 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular component transfer between photoreceptor cells of the retina.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2025 Jan;104:101317. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2024.101317. Epub 2024 Nov 16. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2025. PMID: 39551387 Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
