Improving parameter recovery for conflict drift-diffusion models
- PMID: 32043224
- PMCID: PMC7575478
- DOI: 10.3758/s13428-020-01366-8
Improving parameter recovery for conflict drift-diffusion models
Abstract
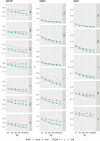
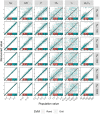
Several drift-diffusion models have been developed to account for the performance in conflict tasks. Although a common characteristic of these models is that the drift rate changes within a trial, their architecture is rather different. Comparative studies usually examine which model fits the data best. However, a good fit does not guarantee good parameter recovery, which is a necessary condition for a valid interpretation of any fit. A recent simulation study revealed that recovery performance varies largely between models and individual parameters. Moreover, recovery was generally not very impressive. Therefore, the aim of the present study was to introduce and test an improved fit procedure. It is based on a grid search for determining the initial parameter values and on a specific criterion for assessing the goodness of fit. Simulations show that not only the fit performance but also parameter recovery improved substantially by applying this procedure, compared to the standard one. The improvement was largest for the most complex model.
Keywords: Drift-diffusion models; Grid-search method; Model-fit procedure; Parameter recovery.
Figures
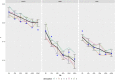
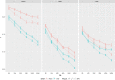
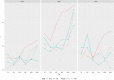


References
-
- Brent RP. Algorithms for function minimization without derivatives. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall; 1973.
-
- De Jong R, Liang CC, Lauber E. Conditional and unconditional automaticity: A dual-process model of effects of spatial stimulus-response correspondence. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance. 1994;20:731–750. - PubMed
-
- Eriksen BA, Eriksen CW. Effects of noise letters upon the identification of a target letter in a nonsearch task. Perception & Psychophysics. 1974;16(1):143–149. doi: 10.3758/BF03203267. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

