Circulating angiopoietin-2 and the risk of mortality in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 10 prospective cohort studies
- PMID: 32043429
- PMCID: PMC7013116
- DOI: 10.1177/1753466620905274
Circulating angiopoietin-2 and the risk of mortality in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 10 prospective cohort studies
Abstract
Background: Angiopoietin-2 (Ang-2), as one of the ligands of endothelial receptor Tie2, is known to be significant for vessel maturation and stabilization after birth. Previous studies showed the relationship between Ang-2 level and the risk of mortality in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). However, the link between circulating Ang-2 and the risk of mortality in patients with ARDS varied in different investigations.
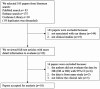
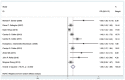
Results: We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis of all available cohort studies regarding the association between baseline circulating Ang-2 and mortality in patients with ARDS. Among the 10 eligible studies, pooled odds ratio (OR) showed that high Ang-2 level contributed to ARDS mortality [OR = 1.56, 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.30-1.89, I2 = 76.2%]. Stratified analysis revealed that higher circulating Ang-2 was related to a 30% higher risk in the high-quality scores group (OR = 1.68, 95% CI: 1.33-2.68, I2 = 62.4%). The I2 of the bad compliance group decreased from 76.2% to 8.5%, which suggested that compliance is a significant source of heterogeneity. This association may be blunted by potential bias, although the results was not meaningfully changed by omitting only one study at a time. Further subgroup analysis and meta-regression support that compliance of patients also affects the results significantly, compared with the publication year, follow-up duration, the samples, or population characteristics.
Conclusion: Participants with higher baseline Ang-2 were at a higher risk for future risk of mortality in patients with ARDS. Higher circulating Ang-2 levels could independently predict the risk of mortality in patients with ARDS. However, further large scale prospective cohorts or even interventional studies are warranted to evaluate the diagnostic power of Ang-2 and its causative role on ARDS outcome. The reviews of this paper are available via the supplemental material section.
Keywords: acute respiratory distress syndrome; angiopoietin-2; meta-analysis; mortality.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Circulating angiopoietin 2 correlates with mortality in a surgical population with acute lung injury/adult respiratory distress syndrome.Shock. 2008 Jun;29(6):656-61. doi: 10.1097/shk.0b013e31815dd92f. Shock. 2008. PMID: 18091573 Free PMC article.
-
[Study on the correlation between angiopoietin-2 and prognosis in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2024 Sep;36(9):962-965. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20240314-00235. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2024. PMID: 39380518 Chinese.
-
Plasma angiopoietin-2 outperforms other markers of endothelial injury in prognosticating pediatric ARDS mortality.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2016 Feb 1;310(3):L224-31. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00336.2015. Epub 2015 Dec 11. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26660787 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review of biomarkers multivariately associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome development and mortality.Crit Care. 2020 May 24;24(1):243. doi: 10.1186/s13054-020-02913-7. Crit Care. 2020. PMID: 32448370 Free PMC article.
-
Mortality in Pediatric Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Intensive Care Med. 2019 Jul;34(7):563-571. doi: 10.1177/0885066617705109. Epub 2017 May 1. J Intensive Care Med. 2019. PMID: 28460591
Cited by
-
The role of angiopoietin-2 and surfactant protein-D levels in SARS-CoV-2-related lung injury: A prospective, observational, cohort study.J Med Virol. 2021 Oct;93(10):6008-6015. doi: 10.1002/jmv.27184. Epub 2021 Jul 16. J Med Virol. 2021. PMID: 34232533 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic angiopoietin-2 assessment predicts survival and chronic course in hospitalized patients with COVID-19.Blood Adv. 2021 Feb 9;5(3):662-673. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2020003736. Blood Adv. 2021. PMID: 33560382 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Biomarkers for Diagnosis and Treatment of ARDS.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Oct 24;13(21):3296. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13213296. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37958192 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2 infection- induced growth factors play differential roles in COVID-19 pathogenesis.Life Sci. 2022 Sep 1;304:120703. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120703. Epub 2022 Jun 11. Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35700841 Free PMC article.
-
Sphingosine-1-Phosphate as Lung and Cardiac Vasculature Protecting Agent in SARS-CoV-2 Infection.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 23;24(17):13088. doi: 10.3390/ijms241713088. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37685894 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Suri C, Jones PF, Patan S, et al. Requisite role of angiopoietin-1, a ligand for the TIE2 receptor, during embryonic angiogenesis. Cell 1996; 87: 1171–1180. - PubMed
-
- Roviezzo F, Tsigkos S, Kotanidou A, et al. Angiopoietin-2 causes inflammation in vivo by promoting vascular leakage. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2005; 314: 738–744. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

