Intensive support for adults with intellectual disability and behaviours that challenge: a survey of provision and service typologies in England
- PMID: 32043438
- PMCID: PMC7176866
- DOI: 10.1192/bjo.2020.2
Intensive support for adults with intellectual disability and behaviours that challenge: a survey of provision and service typologies in England
Abstract
Background: Approximately 18% of adults with intellectual disabilities living in the community display behaviours that challenge. Intensive support teams (ISTs) have been recommended to provide high-quality responsive care aimed at avoiding unnecessary admissions and reducing lengthy in-patient stays.
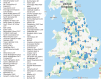
Aims: To identify and describe the geographical distribution and characteristics of ISTs, and to develop a typology of IST service models in England.
Method: We undertook a national cross-sectional survey of 73 ISTs. A hierarchical cluster analysis was performed based on six prespecified grouping factors (mode of referrals, size of case-load, use of outcome measures, staff composition, hours of operation and setting of service). A simplified form of thematic analysis was used to explore free-text responses.
Results: Cluster analysis identified two models of IST provision: (a) independent and (b) enhanced provision based around a community intellectual disability service. ISTs aspire to adopt person-centred care, mostly use the framework of positive behaviour support for behaviour that challenges, and report concerns about organisational and wider context issues.
Conclusions: This is the first study to examine the delivery of intensive support to people with intellectual disability and behaviour that challenges. A two-cluster model of ISTs was found to have statistical validity and clinical utility. The clinical heterogeneity indicates that further evaluation of these service models is needed to establish their clinical and cost-effectiveness.
Keywords: ID services; Intellectual disabilities; adults; behaviour that challenges; intensive support.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical and cost evaluation of intensive support team (IST) models for adults with intellectual disabilities who display challenging behaviour: a comparative cohort study protocol.BMJ Open. 2021 Mar 30;11(3):e043358. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-043358. BMJ Open. 2021. PMID: 33785489 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and cost evaluation of two models of specialist intensive support teams for adults with intellectual disabilities who display behaviours that challenge: the IST-ID mixed-methods study.BJPsych Open. 2023 Jun 26;9(4):e116. doi: 10.1192/bjo.2023.74. BJPsych Open. 2023. PMID: 37357806 Free PMC article.
-
Stakeholder perspectives on intensive support teams for adults with intellectual disabilities who display behaviour that challenges in England.J Appl Res Intellect Disabil. 2023 Sep;36(5):1101-1112. doi: 10.1111/jar.13129. Epub 2023 Jun 4. J Appl Res Intellect Disabil. 2023. PMID: 37271584
-
Intensive support teams for adults with intellectual disabilities displaying challenging behaviour: the IST-ID mixed-methods study.Southampton (UK): National Institute for Health and Care Research; 2022 Nov. Southampton (UK): National Institute for Health and Care Research; 2022 Nov. PMID: 36378807 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Improving support and planning ahead for older people with learning disabilities and family carers: a mixed-methods study.Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2024 Jun;12(16):1-161. doi: 10.3310/MTHW2644. Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2024. PMID: 38940476
Cited by
-
Clinical and cost evaluation of intensive support team (IST) models for adults with intellectual disabilities who display challenging behaviour: a comparative cohort study protocol.BMJ Open. 2021 Mar 30;11(3):e043358. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-043358. BMJ Open. 2021. PMID: 33785489 Free PMC article.
-
An investigation into the critical ingredients of intensive support teams for adults with intellectual disabilities who display challenging behaviour.BJPsych Bull. 2023 Dec 11;49(1):1-6. doi: 10.1192/bjb.2023.94. Online ahead of print. BJPsych Bull. 2023. PMID: 38073278 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and cost evaluation of two models of specialist intensive support teams for adults with intellectual disabilities who display behaviours that challenge: the IST-ID mixed-methods study.BJPsych Open. 2023 Jun 26;9(4):e116. doi: 10.1192/bjo.2023.74. BJPsych Open. 2023. PMID: 37357806 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping and identifying service models for community-based services for children with intellectual disabilities and behaviours that challenge in England.BMC Health Serv Res. 2023 Dec 4;23(1):1354. doi: 10.1186/s12913-023-10388-9. BMC Health Serv Res. 2023. PMID: 38049861 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bowring DL, Totsika V, Hastings RP, Toogood S, Griffith GM. Challenging behaviours in adults with an intellectual disability: a total population study and exploration of risk indices. Br J Clin Psychol 2017; 56: 16–32. - PubMed
-
- NHS England. Transforming Care Model Service Specifications: Supporting Implementation of the Service Models. NHS England, 2017. (https://www.england.nhs.uk/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/model-service-spec...).
-
- O'Dwyer C, McCallion P, Burke É, Carroll R, O'Dwyer M, McCarron M. Prevalence and associated factors of problem behaviours among older adults with intellectual disabilities in Ireland. Res Dev Disabil 2018; 80: 192–204. - PubMed
-
- Hassiotis A, Parkes C, Jones L, Fitzgerald B, Romeo R. Individual characteristics and service expenditure on challenging behaviour for adults with intellectual disabilities. J Appl Res Intellect Disabil 2008; 21: 438–45.
-
- Rose J, Nelson L. A preliminary exploration of the Challenging Behaviour Perception Questionnaire: a measure of parental cognitions about challenging behaviour. J Intellect Dev Disabil 2018; 43: 223–31.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources