miR-155 overexpression is followed by downregulation of its target gene, NFE2L2, and altered pattern of VEGFA expression in the liver of melanoma B16-bearing mice at the premetastatic stage
- PMID: 32043657
- PMCID: PMC7042756
- DOI: 10.1111/iep.12342
miR-155 overexpression is followed by downregulation of its target gene, NFE2L2, and altered pattern of VEGFA expression in the liver of melanoma B16-bearing mice at the premetastatic stage
Abstract
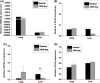
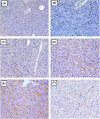
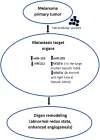
MicroRNAs are involved in the control of tumour progression and in metastatic cascade dynamics. However, the role of microRNAs in distant organ reorganization at the premetastatic stage is less clear, although the process of premetastatic niche formation is a crucial event according to modern concepts of tumour dissemination. The role of the present study was to investigate the expression levels of miR-155, miR-21, miR-205 and miR-let7b, as well as that of their target genes, in target organs of melanoma metastasis at the premetastatic stage. The expression levels of both the pro-oncogenic miR-155 and the tumour suppressive miR-205 were found to be altered in the premetastatic liver of melanoma B16-bearing mice. Bioinformatics analysis identified the target genes of miR-155 to be nuclear factor, erythroid 2 like 2 (NFE2L2), secretogranin II, miR-205, semaphorin 5A and vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA). Among those, the redox status regulatory factor NFE2L2 was downregulated, which corresponded to increased levels of miR-155. Due to the ability of pro-oxidative events to initiate angiogenesis, VEGFA levels were evaluated in the premetastatic liver by immunohistochemistry, which revealed increased VEGFA expression in the central parts of the organ and diminished expression in the periphery. Taken together, these findings may support the concept of functional organ reorganization due to melanoma progression.
Keywords: erythroid 2 like 2; melanoma; metastasis; miR-155; miR-205; nuclear factor; vascular endothelial growth factor A.
© 2020 The Authors. International Journal of Experimental Pathology © 2020 International Journal of Experimental Pathology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
VEGFA and NFE2L2 Gene Expression and Regulation by MicroRNAs in Thyroid Papillary Cancer and Colloid Goiter.Genes (Basel). 2020 Aug 19;11(9):954. doi: 10.3390/genes11090954. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32824922 Free PMC article.
-
The miR-30 Family Inhibits Pulmonary Vascular Hyperpermeability in the Premetastatic Phase by Direct Targeting of Skp2.Clin Cancer Res. 2015 Jul 1;21(13):3071-80. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-2785. Epub 2015 Mar 25. Clin Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25810374
-
Regulation of VEGFA, KRAS, and NFE2L2 Oncogenes by MicroRNAs in Head and Neck Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 5;23(13):7483. doi: 10.3390/ijms23137483. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35806488 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs as regulators of VEGFA and NFE2L2 in cancer.Gene. 2020 Oct 30;759:144994. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2020.144994. Epub 2020 Jul 25. Gene. 2020. PMID: 32721475 Review.
-
MiR-130b/TNF-α/NF-κB/VEGFA loop inhibits prostate cancer angiogenesis.Clin Transl Oncol. 2020 Jan;22(1):111-121. doi: 10.1007/s12094-019-02217-5. Epub 2019 Oct 30. Clin Transl Oncol. 2020. PMID: 31667686
Cited by
-
The dual role of Nrf2 in melanoma: a systematic review.BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2023 Feb 6;24(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s12860-023-00466-5. BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 36747120 Free PMC article.
-
Reactive oxygen species/glutathione dual sensitive nanoparticles with encapsulation of miR155 and curcumin for synergized cancer immunotherapy.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Jul 8;22(1):400. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02575-5. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 38972995 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA MIR205HG regulates melanomagenesis via the miR-299-3p/VEGFA axis.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Feb 1;13(4):5297-5311. doi: 10.18632/aging.202450. Epub 2021 Feb 1. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 33535182 Free PMC article.
-
SEMAPHORINS and their receptors: focus on the crosstalk between melanoma and hypoxia.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Apr 15;40(1):131. doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-01929-3. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33858502 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Hepatic Pre-Metastatic Niche.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jul 31;14(15):3731. doi: 10.3390/cancers14153731. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35954395 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wilmott JS, Tembe V, Howle JR, et al. Intratumoral molecular heterogeneity in a BRAF‐mutant BRAF inhibitor‐resistant melanoma: a case illustrating the challenges for personalized medicine. Mol Cancer Ther. 2012;11:2704‐2708. - PubMed
-
- Peinado H, Zhang H, Matei IR, et al. Pre‐metastatic niches: organ‐specific homes for metastases. Nat Rev Cancer. 2017;17(5):302‐317. - PubMed
-
- Liu Y, Cao X. Characteristics and significance of the pre‐metastatic niche. Cancer Cell. 2016;30:668‐681. - PubMed
-
- van Rooij E. The art of microRNA research. Circ Res. 2011;108:219‐234. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

