Development of neural oscillatory activity in response to speech in children from 4 to 6 years old
- PMID: 32043677
- PMCID: PMC7685108
- DOI: 10.1111/desc.12947
Development of neural oscillatory activity in response to speech in children from 4 to 6 years old
Abstract
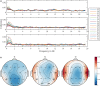
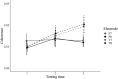
Recent neurophysiological theories propose that the cerebral hemispheres collaborate to resolve the complex temporal nature of speech, such that left-hemisphere (or bilateral) gamma-band oscillatory activity would specialize in coding information at fast rates (phonemic information), whereas right-hemisphere delta- and theta-band activity would code for speech's slow temporal components (syllabic and prosodic information). Despite the relevance that neural entrainment to speech might have for reading acquisition and for core speech perception operations such as the perception of intelligible speech, no study had yet explored its development in young children. In the current study, speech-brain entrainment was recorded via EEG in a cohort of children at three different time points since they were 4-5 to 6-7 years of age. Our results showed that speech-brain entrainment occurred only at delta frequencies (0.5 Hz) at all testing times. The fact that, from the longitudinal perspective, coherence increased in bilateral temporal electrodes suggests that, contrary to previous hypotheses claiming for an innate right-hemispheric bias for processing prosodic information, at 7 years of age the low-frequency components of speech are processed in a bilateral manner. Lastly, delta speech-brain entrainment in the right hemisphere was related to an indirect measure of intelligibility, providing preliminary evidence that the entrainment phenomenon might support core linguistic operations since early childhood.
Keywords: coherence; language development; language lateralization; neural entrainment; reading acquisition; speech perception.
© 2020 The Authors. Developmental Science published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Anthony, J. L. , & Francis, D. J. (2005). Development of phonological awareness. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 14(5), 255–259. 10.1111/j.0963-7214.2005.00376.x - DOI
-
- Baayen, R. H. , Davidson, D. J. , & Bates, D. M. (2008). Mixed‐effects modeling with crossed random effects for subjects and items. Journal of Memory and Language, 59(4), 390–412. 10.1016/j.jml.2007.12.005 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

