Mechanistic Studies of Bioorthogonal ATP Analogues for Assessment of Histidine Kinase Autophosphorylation
- PMID: 32043868
- PMCID: PMC8712274
- DOI: 10.1021/acschembio.9b01024
Mechanistic Studies of Bioorthogonal ATP Analogues for Assessment of Histidine Kinase Autophosphorylation
Abstract
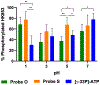
Phosphorylation is an essential protein modification and is most commonly associated with hydroxyl-containing amino acids via an adenosine triphosphate (ATP) substrate. The last decades have brought greater appreciation to the roles that phosphorylation of myriad amino acids plays in biological signaling, metabolism, and gene transcription. Histidine phosphorylation occurs in both eukaryotes and prokaryotes but has been shown to dominate signaling networks in the latter due to its role in microbial two-component systems. Methods to investigate histidine phosphorylation have lagged behind those to study serine, threonine, and tyrosine modifications due to its inherent instability and the historical view that this protein modification was rare. An important strategy to overcome the reactivity of phosphohistidine is the development of substrate-based probes with altered chemical properties that improve modification longevity but that do not suffer from poor recognition or transfer by the protein. Here, we present combined experimental and computational studies to better understand the molecular requirements for efficient histidine phosphorylation by comparison of the native kinase substrate, ATP, and alkylated ATP derivatives. While recognition of the substrates by the histidine kinases is an important parameter for the formation of phosphohistidine derivatives, reaction sterics also affect the outcome. In addition, we found that stability of the resulting phosphohistidine moieties correlates with the stability of their hydrolysis products, specifically with their free energy in solution. Interestingly, alkylation dramatically affects the stability of the phosphohistidine derivatives at very acidic pH values. These results provide critical mechanistic insights into histidine phosphorylation and will facilitate the design of future probes to study enzymatic histidine phosphorylation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
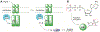


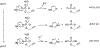
Similar articles
-
A Quantitative Method for the Measurement of Protein Histidine Phosphorylation.Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2077:51-61. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9884-5_4. Methods Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 31707651
-
Exploration of the Effects of γ-Phosphate-Modified ATP Analogues on Histidine Kinase Autophosphorylation.Biochemistry. 2018 Jul 24;57(29):4368-4373. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.8b00485. Epub 2018 Jul 11. Biochemistry. 2018. PMID: 29944360 Free PMC article.
-
Protein histidine phosphorylation: increased stability of thiophosphohistidine.Protein Sci. 1999 Oct;8(10):2177-85. doi: 10.1110/ps.8.10.2177. Protein Sci. 1999. PMID: 10548064 Free PMC article.
-
The many ways that nature has exploited the unusual structural and chemical properties of phosphohistidine for use in proteins.Biochem J. 2021 Oct 15;478(19):3575-3596. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20210533. Biochem J. 2021. PMID: 34624072 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A journey from phosphotyrosine to phosphohistidine and beyond.Mol Cell. 2022 Jun 16;82(12):2190-2200. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2022.05.007. Epub 2022 Jun 1. Mol Cell. 2022. PMID: 35654043 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bioorthogonal Reactions in Bioimaging.Top Curr Chem (Cham). 2024 Feb 24;382(1):7. doi: 10.1007/s41061-024-00452-1. Top Curr Chem (Cham). 2024. PMID: 38400853 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Silico Study, Protein Kinase Inhibition and Molecular Docking Study of Benzimidazole Derivatives.Bioinform Biol Insights. 2024 Jun 6;18:11779322241247635. doi: 10.1177/11779322241247635. eCollection 2024. Bioinform Biol Insights. 2024. PMID: 38854784 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of small molecule kinase inhibitors as novel antimicrobial and antibiofilm agents.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2021 Dec;98(6):1038-1064. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.13962. Epub 2021 Oct 4. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2021. PMID: 34581492 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activity-based protein profiling in microbes and the gut microbiome.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2023 Oct;76:102351. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2023.102351. Epub 2023 Jul 8. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2023. PMID: 37429085 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Molecular Mechanism of Fludioxonil Action Is Different to Osmotic Stress Sensing.J Fungi (Basel). 2021 May 17;7(5):393. doi: 10.3390/jof7050393. J Fungi (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34067802 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Potel CM, Lin MH, Heck AJR, and Lemeer S (2018) Widespread bacterial protein histidine phosphorylation revealed by mass spectrometry-based proteomics. Nat. Methods 15, 187–190. - PubMed
-
- Makwana MV, Muimo R, and Jackson RFW (2018) Advances in development of new tools for the study of phosphohistidine. Lab. Invest 98, 291. - PubMed
-
- Matthews HR (1995) Protein kinases and phosphatases that act on histidine, lysine, or arginine residues in eukaryotic proteins: A possible regulator of the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade. Pharmacol. Ther 67, 323–350. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

