Mechanisms of Fibrosis Development in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis
- PMID: 32044315
- PMCID: PMC7682538
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.11.311
Mechanisms of Fibrosis Development in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis
Abstract
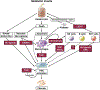
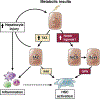
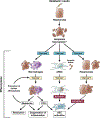
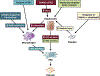
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is the most prevalent liver disease worldwide, affecting 20%-25% of the adult population. In 25% of patients, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease progresses to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which increases the risk for the development of cirrhosis, liver failure, and hepatocellular carcinoma. In patients with NASH, liver fibrosis is the main determinant of mortality. Here, we review how interactions between different liver cells culminate in fibrosis development in NASH, focusing on triggers and consequences of hepatocyte-macrophage-hepatic stellate cell (HSC) crosstalk. We discuss pathways through which stressed and dead hepatocytes instigate the profibrogenic crosstalk with HSC and macrophages, including the reactivation of developmental pathways such as TAZ, Notch, and hedgehog; how clearance of dead cells in NASH via efferocytosis may affect inflammation and fibrogenesis; and insights into HSC and macrophage heterogeneity revealed by single-cell RNA sequencing. Finally, we summarize options to therapeutically interrupt this profibrogenic hepatocyte-macrophage-HSC network in NASH.
Keywords: Drug Development; Metabolic Syndrome; Noninvasive Biomarkers; Pediatric Obesity.
Copyright © 2020 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Younossi Z, Anstee QM, Marietti M, Hardy T, Henry L, Eslam M, George J, Bugianesi E. Global burden of NAFLD and NASH: trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2018;15:11–20. - PubMed
-
- Wong RJ, Aguilar M, Cheung R, Perumpail RB, Harrison SA, Younossi ZM, Ahmed A. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis is the second leading etiology of liver disease among adults awaiting liver transplantation in the United States. Gastroenterology 2015;148:547–55. - PubMed
-
- Diehl AM, Day C. Cause, Pathogenesis, and Treatment of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. N Engl J Med 2017;377:2063–2072. - PubMed
-
- Schuppan D, Pinzani M. Anti-fibrotic therapy: lost in translation? J Hepatol 2012;56 Suppl 1:S66–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

