Omega-3 Self-Nanoemulsion Role in Gastroprotection against Indomethacin-Induced Gastric Injury in Rats
- PMID: 32045979
- PMCID: PMC7076357
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12020140
Omega-3 Self-Nanoemulsion Role in Gastroprotection against Indomethacin-Induced Gastric Injury in Rats
Retraction in
-
RETRACTED: Ahmed et al. Omega-3 Self-Nanoemulsion Role in Gastroprotection against Indomethacin-Induced Gastric Injury in Rats. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 140.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Jan 29;16(2):192. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16020192. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38399354 Free PMC article.
Abstract
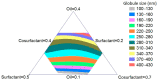
Peptic ulcer disease is an injury of the alimentary tract that leads to a mucosal defect reaching the submucosa. This study aimed to formulate and optimize omega-3 oil as a self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system (SNEDDS) to achieve oil dispersion in the nano-range in the stomach to augment omega-3 oil gastric ulcer protection efficacy. Three SNEDDS components were selected as the design factors: the concentrations of the oil omega-3 (X1, 10-30%), the surfactant tween 20 and Kolliphor mixture (X2, 20-40%), and the cosurfactant transcutol (X3, 40-60%). The mixture experimental design proposed twenty-three formulations with varying omega-3 SNEDDS formulation component percentages. The optimized omega-3 SNEDDS formula was investigated for gastric ulcer protective effects by evaluating the ulcer index and by the determination of gastric mucosa oxidative stress parameters. Results revealed that optimized omega-3-SNEDDS achieved significant improvement in the gastric ulcer index in comparison with pure omega-3 oil. Histopathological findings confirmed the protective effect of the formulated optimized omega-3 SNEDDS in comparison with omega-3 oil. These findings suggest that formulation of omega-3 in the form of a SNEDDS would be more effective in gastric ulcer protection than the administration of omega-3 as a crude oil.
Keywords: factorial design; fish oil; gastric ulcer; nanoemulsion; natural product.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders/company had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

