Identification of Potentially Therapeutic Target Genes of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 32046048
- PMCID: PMC7037431
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph17031053
Identification of Potentially Therapeutic Target Genes of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a major threat to public health. However, few effective therapeutic strategies exist. We aimed to identify potentially therapeutic target genes of HCC by analyzing three gene expression profiles.
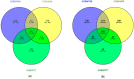
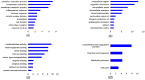
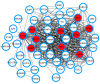
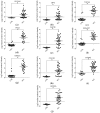
Methods: The gene expression profiles were analyzed with GEO2R, an interactive web tool for gene differential expression analysis, to identify common differentially expressed genes (DEGs). Functional enrichment analyses were then conducted followed by a protein-protein interaction (PPI) network construction with the common DEGs. The PPI network was employed to identify hub genes, and the expression level of the hub genes was validated via data mining the Oncomine database. Survival analysis was carried out to assess the prognosis of hub genes in HCC patients.
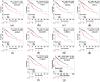
Results: A total of 51 common up-regulated DEGs and 201 down-regulated DEGs were obtained after gene differential expression analysis of the profiles. Functional enrichment analyses indicated that these common DEGs are linked to a series of cancer events. We finally identified 10 hub genes, six of which (OIP5, ASPM, NUSAP1, UBE2C, CCNA2, and KIF20A) are reported as novel HCC hub genes. Data mining the Oncomine database validated that the hub genes have a significant high level of expression in HCC samples compared normal samples (t-test, p < 0.05). Survival analysis indicated that overexpression of the hub genes is associated with a significant reduction (p < 0.05) in survival time in HCC patients.
Conclusions: We identified six novel HCC hub genes that might be therapeutic targets for the development of drugs for some HCC patients.
Keywords: MCC algorithm; PPI network; gene expression profile; hepatocellular carcinoma; hub gene.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Integrated Bioinformatics Analysis for the Screening of Hub Genes and Therapeutic Drugs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2023;24(8):1035-1058. doi: 10.2174/1389201023666220628113452. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 35762549
-
Identification of Multiple Hub Genes and Pathways in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Bioinformatics Analysis.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Jul 12;2021:8849415. doi: 10.1155/2021/8849415. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34337056 Free PMC article.
-
Screening Hub Genes as Prognostic Biomarkers of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Bioinformatics Analysis.Cell Transplant. 2019 Dec;28(1_suppl):76S-86S. doi: 10.1177/0963689719893950. Epub 2019 Dec 11. Cell Transplant. 2019. PMID: 31822116 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying hepatocellular carcinoma-related hub genes by bioinformatics analysis and CYP2C8 is a potential prognostic biomarker.Gene. 2019 May 25;698:9-18. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2019.02.062. Epub 2019 Feb 27. Gene. 2019. PMID: 30825595
-
Identification of most representative hub-genes for diagnosis, prognosis, and therapies of hepatocellular carcinoma.Chin Clin Oncol. 2024 Jun;13(3):32. doi: 10.21037/cco-23-151. Chin Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38984486
Cited by
-
The neurological and non-neurological roles of the primary microcephaly-associated protein ASPM.Front Neurosci. 2023 Aug 3;17:1242448. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1242448. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37599996 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive analysis of prognostic value and immune infiltration of Regulator of Chromosome Condensation 2 in lung adenocarcinoma.J Cancer. 2024 Feb 11;15(7):1901-1915. doi: 10.7150/jca.91367. eCollection 2024. J Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38434981 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Hub Genes Associated With Hepatocellular Carcinoma Using Robust Rank Aggregation Combined With Weighted Gene Co-expression Network Analysis.Front Genet. 2020 Sep 30;11:895. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00895. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 33133125 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Value of EZH2 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Its Potential for Target Therapy.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Jan 20;58(2):155. doi: 10.3390/medicina58020155. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 35208478 Free PMC article.
-
The role and therapeutic value of NUSAP1 in human cancers.J Transl Med. 2025 Jul 2;23(1):725. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06746-2. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40605080 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

