Evolving Cell-Based and Cell-Free Clinical Strategies for Treating Severe Human Liver Diseases
- PMID: 32046114
- PMCID: PMC7072646
- DOI: 10.3390/cells9020386
Evolving Cell-Based and Cell-Free Clinical Strategies for Treating Severe Human Liver Diseases
Abstract
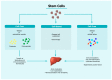
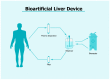
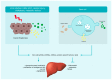
Liver diseases represent a major global health issue, and currently, liver transplantation is the only viable alternative to reduce mortality rates in patients with end-stage liver diseases. However, scarcity of donor organs and risk of recidivism requiring a re-transplantation remain major obstacles. Hence, much hope has turned towards cell-based therapy. Hepatocyte-like cells obtained from embryonic stem cells or adult stem cells bearing multipotent or pluripotent characteristics, as well as cell-based systems, such as organoids, bio-artificial liver devices, bioscaffolds and organ printing are indeed promising. New approaches based on extracellular vesicles are also being investigated as cell substitutes. Extracellular vesicles, through the transfer of bioactive molecules, can modulate liver regeneration and restore hepatic function. This review provides an update on the current state-of-art cell-based and cell-free strategies as alternatives to liver transplantation for patients with end-stage liver diseases.
Keywords: cell therapy; extracellular vesicles; liver diseases; organ printing; organoids; scaffolds; transplantation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pluripotent-Stem-Cell-Derived Hepatic Cells: Hepatocytes and Organoids for Liver Therapy and Regeneration.Cells. 2020 Feb 12;9(2):420. doi: 10.3390/cells9020420. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32059501 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell-based liver therapies: past, present and future.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2018 Jul 5;373(1750):20170229. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2017.0229. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29786563 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Application of Pluripotent Stem Cells: An Alternative Cell-Based Therapy for Treating Liver Diseases?Transplantation. 2016 Dec;100(12):2548-2557. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000001426. Transplantation. 2016. PMID: 27495745 Review.
-
Present and Future Perspectives of Using Human-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells and Organoid Against Liver Failure.Cell Transplant. 2019 Dec;28(1_suppl):160S-165S. doi: 10.1177/0963689719888459. Epub 2019 Dec 16. Cell Transplant. 2019. PMID: 31838891 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell therapy in end-stage liver disease: replace and remodel.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023 May 25;14(1):141. doi: 10.1186/s13287-023-03370-z. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 37231461 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of the Microenvironment in Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Based Strategies for Treating Human Liver Diseases.Stem Cells Int. 2021 Nov 16;2021:5513309. doi: 10.1155/2021/5513309. eCollection 2021. Stem Cells Int. 2021. PMID: 34824587 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of mesenchymal stem cells in liver fibrosis and regeneration.Liver Res. 2024 Nov 26;8(4):246-258. doi: 10.1016/j.livres.2024.11.004. eCollection 2024 Dec. Liver Res. 2024. PMID: 39958916 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of Preoperative NANOG-Positive Circulating Tumor Cell Levels With Recurrence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2021 May 27;11:601668. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.601668. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34123777 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced effects of slowly co-released TGF-β3 and BMP-2 from biomimetic calcium phosphate-coated silk fibroin scaffolds in the repair of osteochondral defects.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Jul 30;22(1):453. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02712-0. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 39080653 Free PMC article.
-
Liver Regeneration and Cell Transplantation for End-Stage Liver Disease.Biomolecules. 2021 Dec 20;11(12):1907. doi: 10.3390/biom11121907. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34944550 Free PMC article. Review.

